
Ophthalmologists at the Filatov Institute of Eye Diseases and Tissue Therapy of the National Academy of Medical Sciences of Ukraine (Odesa) performed the world’s first surgery to remove an intraocular hemangioma in a child. For the first time in the world, the Filatov National Institute of Robotics and Tissue Therapy of the National Academy of Medical Sciences of Ukraine (Odesa) performed a surgery to remove a large intraocular choroidal hemangioma in a child.
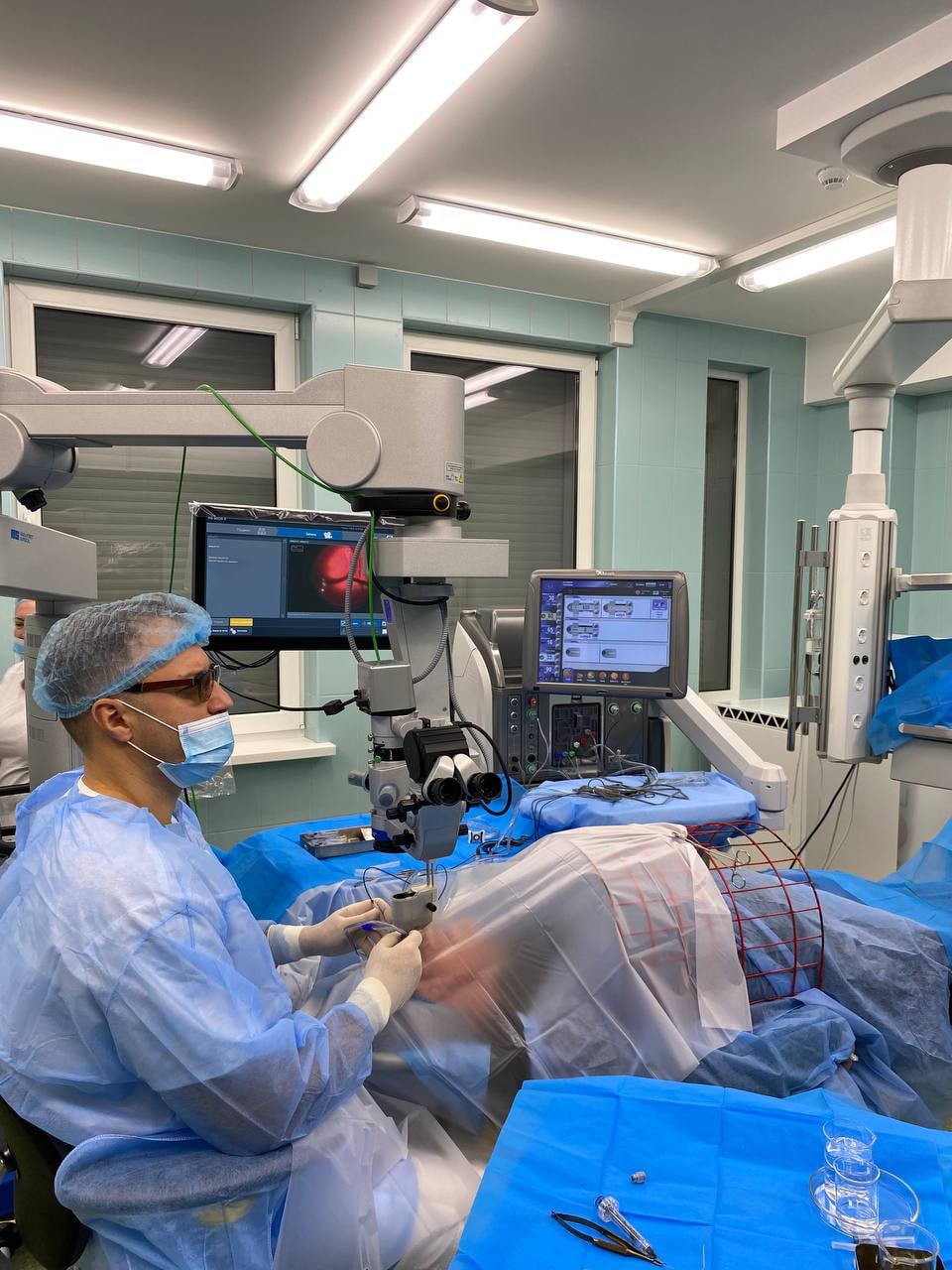
The institute told Interfax-Ukraine that the operation was performed by Mykola Umanets, MD, head of the Department of Retinal and Vitreous Pathology.
“Surgical removal of intraocular hemangiomas is not performed due to the very high risk of bleeding and the lack of effective methods to stop it. All modern methods of treating intraocular hemangiomas are aimed at stopping the growth and destruction of the tumor and are effective in the case of small tumors. In cases of large tumors, the only way to solve the problem is to remove the eye,” the institute emphasized.
The operation was performed on a 13-year-old patient. In August 2023, during an eye examination before school, the patient complained of a partial loss of visual field, but there were no complaints of visual impairment and he did not seek medical attention. During the examination in August 2024, doctors found that the vision in the left eye had significantly decreased. During the examination at the Filatov Institute, an almost complete detachment of the retina and a hemangioma under it were found. The situation was complicated by the patient’s young age (at a young age, tumors grow rapidly and behave much more aggressively), untimely treatment, large size of the tumor and unfortunate location almost close to the optic nerve, development of a large retinal detachment with loss of vision.
In 2020, the Filatov Institute removed a large hemangioma from an adult patient for the first time in the world, and it was also the first in the world.
“Just like in 2020, we relied on a unique method of high-frequency electric welding of biological tissues in ophthalmology, developed by scientists of the Filatov Institute together with specialists of the E.O. Paton Institute of Electric Welding, which allows us to remove a hemangioma in an adult patient at the Filatov Institute. The new method allows to remove a hemangioma in an adult patient at the E.O. Paton Institute and significantly reduces the risk of bleeding with the help of unique tools developed by specialists of the two institutes. During the operation, each dissected vessel was “brewed” to prevent bleeding,” the institute noted.
Hemangiomas are benign tumors in various parts of the body caused by abnormal growth of blood vessels and are practically penetrated by them. Hemangiomas can also form in the internal organs, in particular (very rarely) in the choroid (choroid). They do not threaten the patient’s life, but are accompanied by a significant decrease in vision and can cause the development of serious complications, such as retinal detachment, hemorrhages in the eye cavity, and increased intraocular pressure (glaucoma).
Prior to the successful surgery performed by the ophthalmologists of the Filatov Institute in 2020, the world had recorded the only case of surgical removal of an intraocular hemangioma: In 2019, Italian ophthalmologist Barbara Parolini performed surgery to remove a small tumor in an adult patient.
Source: https://interfax.com.ua/

The Filatov Institute of Eye Diseases and Tissue Therapy of the National Academy of Medical Sciences of Ukraine (Odesa) for the first time in the world conducted a unique operation to remove a large intraocular hemangioma of the choroid.
According to a press release of the institute, the operation was performed at the end of 2020 on a 21-year-old patient due to the impossibility of using non-surgical methods of treatment because of the large tumor size (12.2 mm x 16.1 mm, bulging into the vitreous humor – 6 mm), which continued to grow.
“Understanding what the loss of an eye would mean for a young active girl, both from a cosmetic and psychological point of view, the doctors of the Filatov Institute offered the patient an operation,” the press release said.
To reduce the risk of bleeding, the specialists of the institute used their unique development – the method of high-frequency welding of biological tissues in ophthalmology, developed jointly with the Paton Institute of Electric Welding of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine. They also developed the tools necessary for the interventions.
The operation was carried out by one of the authors of the method, Doctor of Medical Sciences Mykola Umanets. During the operation, which lasted several hours, each dissected vessel was “welded” to prevent bleeding.
“When the patient came for a check-up a month later, the doctors were not only convinced that they had managed to save the eye, but also revealed the appearance of her “silhouette vision,” which was not there before the operation,” the press release said.
At present, the institute’s specialists are preparing publications for world-famous ophthalmological editions. The video filming made during the operation will allow presenting a unique achievement at the world conferences and congresses.
Hemangioma is benign neoplasms that affect the blood vessels of a person in various parts of the body. In the case of formation in the choroid of the eye, they do not threaten the patient’s life, however, they are accompanied by a significant decrease in vision and can cause the development of serious complications, such as retinal detachment, hemorrhage into the eye cavity, increased intraocular pressure (glaucoma).
Currently, there are a number of treatment methods for this pathology, aimed at stopping the growth and destruction of the tumor and are effective in the case of small formations. The only attempt to surgically remove an intraocular hemangioma recorded by the world ophthalmological community is an operation performed in 2019 by Italian ophthalmologist Barbara Parolini. In that case, the tumor was small. In the case of a large lesion and/or its unsuccessful location, surgical removal of intraocular hemangiomas is not performed due to a very high risk of bleeding and a lack of effective methods to stop it. Most often, the only way to solve the problem is to remove the eye.