
According to Serbian Economist, the energy partnership between Belgrade and Baku is rapidly moving beyond symbolic diversification and beginning to transform into a separate supply chain capable of significantly influencing the balance of the Serbian gas market. Azerbaijan’s Deputy Minister of Energy Orkhan Zeynalov said that by the end of 2026 – early 2027, Azerbaijan could cover up to 20% of Serbia’s gas needs, which, according to him, directly strengthens energy security by reducing dependence on a single source.
The context is simple: Serbia has remained predominantly dependent on gas imports in recent years, and the issue of diversification has become part of a broader agenda, ranging from heating and electricity prices to negotiations with the EU on energy integration. Reuters previously estimated that Serbia receives about 80% of its gas from Russia, with alternative volumes currently serving as insurance and a bargaining chip.
The legal framework for the Azerbaijani route has already been established. The contract between SOCAR and Srbijagas, signed in November 2023, provides for the supply of up to 400 million cubic meters per year in 2024-2026, with the possibility of increasing volumes after 2027. At the same time, official statements by the governments of Serbia and Azerbaijan have recorded separate seasonal agreements for additional volumes during the winter period.
Actual deliveries from Azerbaijan began in 2024, but so far have remained small compared to the overall market. According to data cited by Azerbaijan’s State Statistics Committee, Serbia received about 72.6 million cubic meters of Azerbaijani gas between February and December 2024. For comparison, according to estimates by Azerbaijani and regional sources, in January-November 2025, supplies had already grown to 192 million cubic meters.
Why is Belgrade taking this more seriously than “just another contract”? Because gas is beginning to be linked to industrial projects. In mid-February 2026, the leaders of Serbia and Azerbaijan confirmed plans to build a 500 MW gas-fired power plant, which is seen as a joint project with an estimated commissioning date of 2029. Industry media estimate the investment at around €600 million. Such a plant is capable of creating stable demand for fuel and, accordingly, pushing forward discussions on long-term supply terms — which is why Baku’s statements separately mention the topic of gas prices for future generation.
The stated target of 15-20% seems realistic precisely as a “market share” rather than the maximum technical capacity of the route. Even with Serbia’s moderate consumption, this means the need to reach several hundred million cubic meters per year on a sustainable basis and to secure a commercial supply formula after 2026. At the same time, Baku is making it clear that it sees Serbia as a potential energy hub for the Western Balkans and is looking for additional areas of cooperation, including projects in the field of green energy and hydrogen.

Naftogaz of Ukraine has attracted an additional €50 million from the European Investment Bank for gas imports, the company said
“Another important step to get through the winter stably. Naftogaz has attracted an additional €50 million in financing from the European Investment Bank,” Naftogaz said in a statement on Telegram on Thursday evening.
According to the statement, these funds will be used to import gas and support the energy system during peak loads, when cold weather and shelling create the greatest pressure.
It is noted that the loan was made possible thanks to the support of the European Commission.
As indicated by Naftogaz, this financing complements the EUR 300 million EIB loan and EUR 127 million in EU grant support with the participation of the Norwegian government that have already been raised.
“It is also important to note that Naftogaz has committed to reinvesting the equivalent of this amount in renewable energy projects,” the company said.

The European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD) and one of the European countries will provide Ukraine with EUR85 million for the purchase of additional gas volumes, First Deputy Prime Minister of Energy Denys Shmyhal said.
“EUR 85 million through EBRD instruments for the purchase of additional gas volumes for Ukraine. Work on obtaining the relevant grant from one of the European countries is already being completed,” Shmyhal wrote on Telegram on Tuesday.
He noted that this was discussed during an online conversation with EBRD President Odile Renaud-Basso.
“We are grateful to our partners for this! We will continue to work together to find additional sources of funding,” the head of the Ministry of Energy emphasized.
According to him, it is also extremely necessary to continue financial support from the EBRD to Ukrenergo and Ukrhydroenergo, as this helps to provide repairs, equipment, and implement new solutions so that people have light and heat.

The prolonged cold spell in Europe is pushing gas prices up. The spot price for “day ahead” delivery on the benchmark European TTF hub closed at $486 per 1,000 cubic meters on Wednesday, adding 11% in just one trading day. This is the highest level since June 2025.
On Thursday, trading opened at $491. At the moment, the price has adjusted to $477.
Air temperatures in Europe in January this year are falling to their lowest levels in the last decade and a half. Overall, January (which is already the coldest winter month) is expected to be three degrees colder than the climatic norm and four degrees colder than last year.
Clear weather is accompanied by low wind speeds, or even calm conditions. This increases the load on the power system, as it reduces the output of wind farms. The reliability of the power system is maintained primarily by underground gas storage facilities, which are the most flexible source and closest to the points of consumption.
The average level of gas reserves in underground storage facilities in Europe fell to 48.4% at the end of the gas day on January 20, according to data from Gas Infrastructure Europe. This is 15 percentage points lower than the average for the last five years. At the moment, European underground gas storage facilities are ahead of the usual rate of consumption by four weeks. Moreover, the GIE observation base knows of examples when such a level (or even much higher – 59%) of reserves was reached only by the end of the withdrawal season and the start of injection.
By the end of 2025, countries in the region had purchased 109 million tons of LNG (142 billion cubic meters in regasified volume), which is 28% more than in 2024. In January 2026, liquefied gas imports could reach 10 million tons, which is 24% higher than a year earlier. And this could be a new record for the European gas industry. Despite high demand, there remains a large unused capacity reserve – on January 20, terminals were operating at 51% of their capacity. There is also a noticeable trend of declining LNG stocks at terminals.

Over the past month, BETS held 117 trading sessions for the purchase and sale of natural gas on the medium- and long-term market, as well as four trading sessions each day on the short-term market.
A total of 304 starting positions were formed at the BETS trading platform for trading resources in December 2025, January 2026, and subsequent months, in the gas transmission system and underground gas storage facilities. A total of approximately 156 million cubic meters of natural gas was sold on the medium- and long-term market. 9.08 million cubic meters of natural gas were sold on the short-term market.
On the medium- and long-term market in December, quoted prices in the section of the same name ranged from UAH 19,140 to UAH 21,250 excluding VAT. There was a downward trend in prices throughout the month. The initiators of the auctions formed starting positions mainly for sale.
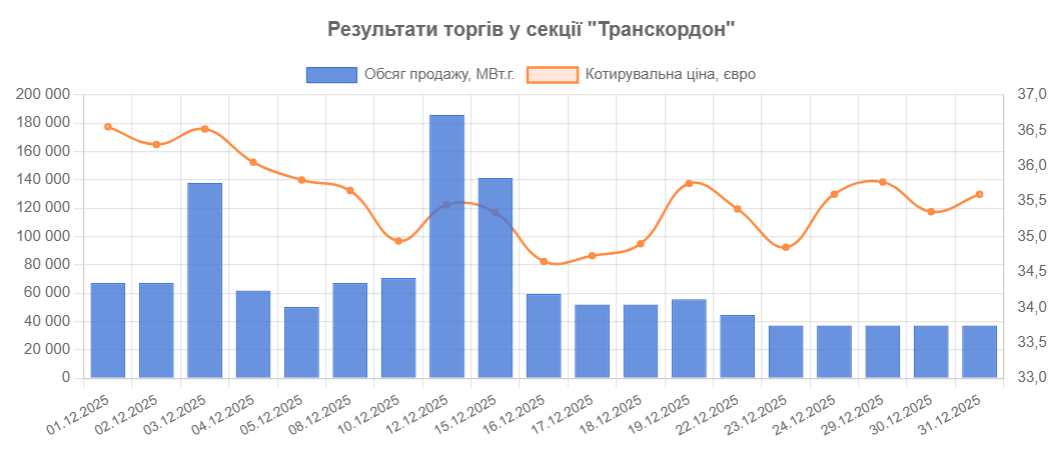
Last month, transactions were concluded in the “Cross-border” section on the terms of delivery at the border point. The total volume of these transactions amounted to 1.3 million MWh at prices ranging from €34.65 to €36.55.
On the short-term market, exchange rates fluctuated daily in the range of UAH 19,227-20,416.26 excluding VAT, with a downward trend. In addition to the intraday market, transactions were concluded on the UEB day-ahead market with a total volume of 360,000 cubic meters.
” December confirmed the consistently high demand for UEB exchange instruments. We will continue to focus on improving the efficiency of trading procedures in general and developing medium-term standardized products in particular, so that participants receive transparent prices and guaranteed execution of transactions,” said UEB CEO Alexander Kovalenko.

The Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine has maintained zero quotas for the export of natural gas of Ukrainian origin in 2026, according to Government Resolution No. 1795 of December 31 on the list of goods whose export and import are subject to licensing and quotas.
According to the document, exports of natural gas of Ukrainian origin in 2026 will continue to be subject to quotas, with the quota set at zero.
The resolution is published on the government’s website.