
The National Bank of Ukraine in its August inflation report worsened its forecast for the country’s 2024 consolidated budget deficit including grants to UAH 1,281 billion, or 16.8% of GDP, down from UAH 811 billion, or 10.5% of GDP, in its April report.
“Deficits are expected to be higher than in the previous forecast, primarily due to the longer duration of security risks, and therefore the need for significant spending on the security and defense sector. Taking this into account, the amount of expected international assistance to finance other expenditures has been increased,” the NBU points out.
In the new report, the forecast of the consolidated budget deficit including grants in 2025 is raised to UAH 883 billion, or 10.0% of GDP, up from UAH 577 billion, or 6.5% of GDP in the April report.
Last year, as the NBU recalled, the deficit of the consolidated budget including grants amounted to UAH 845 billion, or 16.3% of GDP. In the second quarter of this year, it widened to more than UAH 233 billion, and excluding grants in revenue – to UAH 369 billion, or more than 24% of GDP.
“In 2023, the budget deficit excluding grants in revenue is expected to be at the level of the previous year – more than 26.3% of GDP. In the future, due to the increase in revenues, it will narrow to almost 20% of GDP in 2024 and 12% of GDP in 2025 excluding revenue grants,” the National Bank summarized.
It specified that it expects grants to decline from 9.3% of GDP last year to 6.5% of GDP this year, 2.9% of GDP next year and 1.8% of GDP in 2025.
“Given the significant budget deficits for several consecutive years and their financing mainly by debt, as well as the reduction of grant support in the medium term, the debt will approach 100% of GDP,” the National Bank said. It explained that it increased the debt-to-GDP ratio in this forecast compared to the previous one due to the revision of assumptions about the size of deficits upward and grant support downward in 2024-2025.
In particular, the NBU expects government debt to rise from 78.4% of GDP to 84.6% of GDP this year, to 96.6% of GDP next year and to 98.2% of GDP in 2025.
“At the same time, such a high level of debt will have a relatively moderate pressure on the budget in the coming years, primarily due to the receipt of loan funds on preferential terms – at low rates and with a deferred schedule of principal payments,” the NBU believes.

Ukraine’s real gross domestic product (GDP) growth in the second quarter of 2023 compared to the same period last year amounted to 18.3% after a decline of 10.5% in the first quarter, such an updated estimate the National Bank of Ukraine published in an inflation report on its website on Friday night.
According to it, the economic recovery will slow to 4.6% in the third quarter of 2023 and 1.8% in the fourth quarter, with a slight acceleration to 2.6-2.2% in the first and second quarters of next year.
In late April, the National Bank expected GDP growth of 15.9% in the second quarter of this year, and 3.9% and 3.7% in the third and fourth quarters, respectively.
Overall, as reported, the NBU improved its forecast for Ukraine’s economic recovery this year to 2.9% from 2.0% in April (including by improving its estimate of the decline in the first quarter from 13.5% to 10.5%), but worsened it for next year to 3.5% from 4.3%.
“The baseline scenario is based on assumptions about Ukraine’s consistent compliance with the obligations of the Extended Fund Facility Program with the IMF, coherent monetary and fiscal policies, gradual leveling of quasi-fiscal imbalances, particularly in the energy sector. Also, the baseline scenario assumes a tangible reduction of security risks from mid-2024, which will contribute to the full unblocking of seaports, reduction of sovereign risk premium and return of forced migrants to Ukraine”, – the National Bank almost verbatim repeated the paragraph of the previous inflation report, but moved the reduction of security risks from the beginning of 2024 to its middle.
Despite this, the key risk to the forecast is still a longer duration and intensity of the war, which could slow economic recovery and worsen inflation and exchange rate expectations, the National Bank emphasizes.
Among other risks, the regulator named a decrease in the volume or loss of rhythmicity of international aid, the resumption of significant power shortages due to further destruction of energy infrastructure, which will limit economic activity and exports and lead to higher imports and demand for foreign currency.
The NBU also pointed out the risks of export logistics constraints due to large-scale terrorist attacks, the emergence of additional budgetary needs and significant quasi-fiscal deficits, particularly in the energy sector; further complications for agro-products exports.
The National Bank estimates the probability of the risk of prolongation of the war and its escalation, as well as eco-terrorism of the occupants, as well as a quarter earlier, at the level of 25% to 50%.
As for the “grain corridor,” which stopped working in June, although the National Bank estimated this risk at 25-50%, now the regulator gives a 15-25% probability of restoring its work and the same value estimates the new risk of continuing food ban by some European countries, which threatens additional losses of $500 million by the end of this year and a possible reduction in crops.
With a probability of 15-25%, the National Bank also assumes such risks as increased emigration and imbalance of public finances (freezing of tariffs on housing and utility services, reduction of international aid, emission financing of the deficit).
The risk of renewed energy deficit due to damage to infrastructure is on the scale of the National Bank, as in April, at up to 15%.
In this report, as well as in the previous one, there is a mention of such a factor as “Marshall Plan”, which can greatly affect and improve the macro outlook, and its probability the central bank kept at 15-25%.

The real growth of Ukraine’s gross domestic product in 2023 may be up to 5%, but given the existing risks, the Ministry of Economy is still conservatively keeping the growth forecast at 2.8%, said Natalia Gorshkova, Director of the Department of Strategic Planning and Macroeconomic Forecasting of the Ministry of Economy.
“In those working calculations that we have, we as well as most experts who gave you forecasts, we see the possibility this year to reach a real growth of about 5%,” she said at the discussion “New macroeconomic forecast for Ukraine: what will be the exchange rate, GDP and inflation”, organized by the Center for Economic Strategy (CES).
At the same time, Gorshkova pointed out that the ministry is not going to change the current forecast of 2.8% yet, as the risks remain quite significant.
“We are part of the budget process, and we would not want to revise the base for budget formation every time, like on a seesaw,” added the representative of the Ministry of Economy.
She specified that earlier the ministry forecasted the growth of Ukraine’s economy this year at 3.2%, but in June it was adjusted to 2.8% due to the destruction of the Kakhovskaya hydroelectric power plant and pessimistic expectations about the future harvest.
“Perhaps we were hasty,” Gorshkova pointed out.
Speaking about longer-range forecasts, the Economy Ministry representative noted that, like most experts, the ministry hopes that the war will end in 2024, and this will stimulate an early recovery in the economy.
“Therefore, according to the current forecasts that we have, we expect 5% growth next year,” said the director of the Department of Strategic Planning and Macroeconomic Forecasting of the Ministry of Economy.
According to her, the main driver of growth is investment dynamics, while the nature of investments will change: military investments will be replaced by investments in infrastructure projects, in projects related to reconstruction, as well as supported by foreign investments, and the return of migrants from abroad.
As for inflation, which the Ministry of Economy expects this year at the level of 14.7%, Gorshkova noted that the forecast of the agency remains also conservative, as the assumption of the possibility of revision of the official hryvnia exchange rate at the end of the year remains.
As reported, the National Bank of Ukraine last week raised the forecast of real GDP growth in Ukraine in 2023 from 2% to 2.9%, but lowered it for 2024 from 4.3% to 3.5%. In addition, the NBU improved its inflation estimate for this year from 14.8% to 10.6%.

The European Central Bank (ECB) upgraded its inflation forecasts for the euro zone from 2023 to 2025, worsening its estimate of GDP growth in the next two years.
According to new forecasts released by the ECB at its meeting on Thursday, consumer price growth in the euro zone will be 5.4% this year, 3% next year and 2.2% in 2025. In March, inflation was expected to be 5.3%, 2.9% and 2.1%, respectively.
Core inflation, which excludes food and energy costs, is expected to be 5.1% this year before slowing to 3% in 2024 and 2.3% in 2025.
The forecast for euro area GDP growth for 2023 has been lowered to 0.9% from the previously assumed 1%, and for next year to 1.5% from 1.6%. The estimate of the economic growth rate in 2025 remained unchanged at 1.6%.
Forecast of dynamics of changes in ukrainian GDP in % for 2022-2025 in relation to previous period
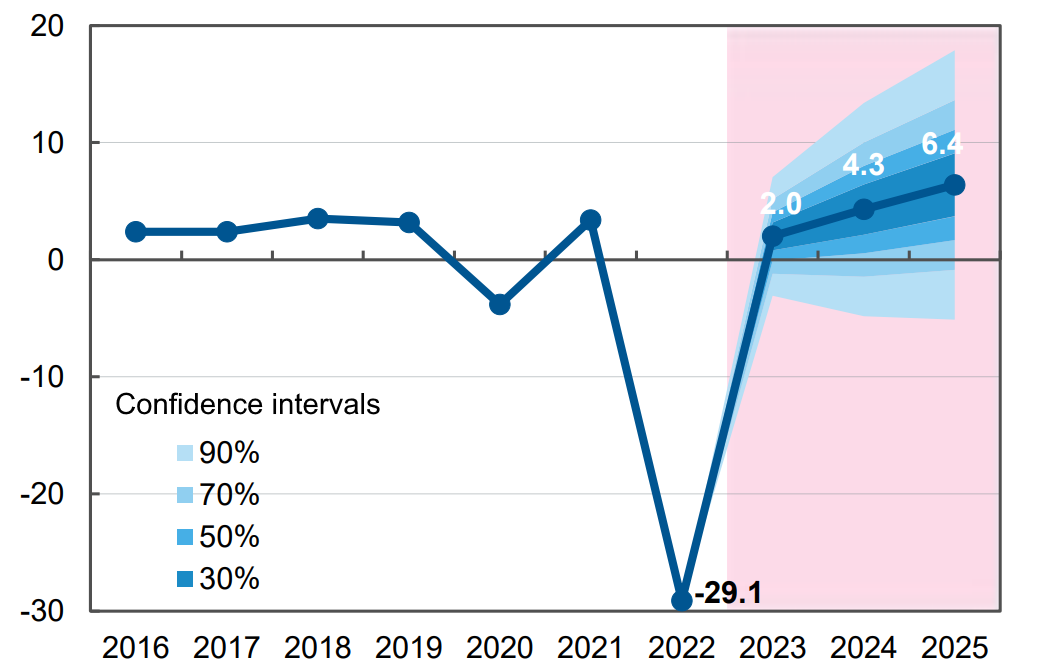
Source: Open4Business.com.ua and experts.news
Real GDP percentage changes over previous period in 2014-2022
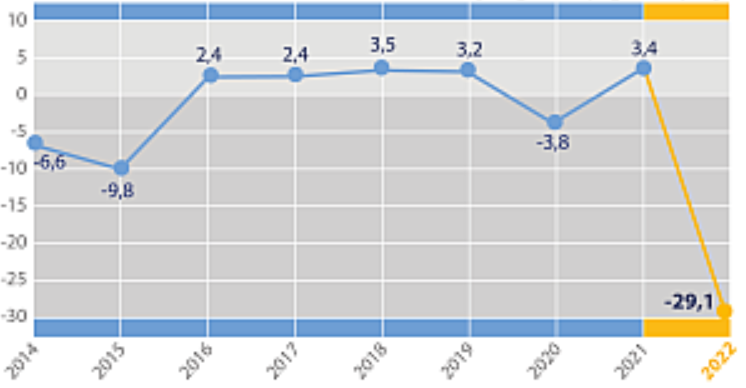
Source: Open4Business.com.ua and experts.news