
Imports of trucks to Ukraine in January-October 2025 increased by 8% in monetary terms compared to the same period in 2024, reaching $819.5 million, according to statistics from the State Customs Service.
According to the published data, the growth rate of imports of this type of vehicle has slowed down again, reaching 11.6% in the first 10 months compared to the same period in 2024.
In October, truck imports fell by 17% compared to October 2024, to $79.2 million, which is also a quarter less than in September 2025.
The largest number of trucks in 10 months was imported from Poland – $149.6 million (1.3% less than last year), France – $133.2 million (43.3% more) and the United States – $104.2 million (30.4% more).
Imports from all other countries in January-October decreased slightly, amounting to $432.6 million.
At the same time, according to statistics, Ukraine exported only $5.6 million worth of trucks in 10 months, mainly to Turkey (62.4% of exports), Romania (32.4%), and Moldova, while a year earlier, exports were even more insignificant ($2.8 million), mainly to Moldova, Poland, and Kazakhstan.
As reported, in 2024, imports of trucks to Ukraine in monetary terms increased by 30% compared to 2023, to $947.84 million, with most of them imported from Poland (almost 20%).

French authorities have completely lifted the travel ban on Telegram founder Pavel Durov and canceled the requirement to regularly report to the police station in Nice, French media reported, citing a judicial source. Earlier in June 2025, the restrictions were eased with permission for short-term trips to Dubai, and now the measures have been completely lifted after “impeccable compliance with judicial control” for a year, Le Monde notes.
Durov was detained in France in August 2024 and placed under judicial control with a bail of €5 million, a ban on leaving the country, and an obligation to report regularly to the police. In the spring and summer of 2025, the court consistently allowed temporary trips to the UAE for up to 14 days. The investigation in France is ongoing and does not constitute an admission of guilt.

Ukraine has been increasing its flax exports for the fourth month in a row amid active demand from exporters. Exports in October amounted to 7.65 thousand tons, which is 26% more than in September this year, according to the information and analytical agency APK-Inform.
Analysts noted that the main buyers of flax are EU countries. In October, 43.1% of supplies were purchased by France, 16.8% by Poland, and 11.4% by Italy.
“The increase in flax exports began in July this year, when the active phase of harvesting this crop began. Thus, flax exports in July were recorded at 1.37 thousand tons, and in August at 3.3 thousand tons,” the experts noted.
A sufficient supply of flax is pushing buyers to lower prices. Thus, the maximum demand prices for flax in Ukrainian ports fell by UAH 800/ton over the month and, as of November 6, usually do not exceed UAH 28,500/ton CPT port, according to APK-Inform.

Imports of trucks to Ukraine in January-September 2025 grew by 11.6% in monetary terms compared to the same period in 2024, reaching $740.18 million, according to statistics from the State Customs Service.
According to the published data, the growth rate of imports of this type of vehicle accelerated, in particular, in the first half of the year, it amounted to 6.2% compared to the same period in 2024.
In September, truck imports increased by 32.7% compared to September 2024, reaching $105.8 million.
Most of the trucks were imported from Poland in the first nine months, accounting for $141.12 million (19% of the total), followed by France with $115 million (15.5%) and the United States with $102.4 million (13.8%).
A year ago, the top three truck supplier countries were the same, with Poland importing $137.8 million, France $78.3 million, and the US $66.2 million.
Imports from all other countries increased slightly in January-September, amounting to $381.7 million.
At the same time, according to statistics, Ukraine exported only $4.4 million worth of trucks in nine months, mainly to Turkey (52.7% of exports), Romania (41%), and Moldova, while a year earlier there were even more insignificant export deliveries ($2.4 million), mainly to Moldova, Poland, and Kazakhstan.
As reported, in 2024, imports of trucks to Ukraine in monetary terms increased by 30% compared to 2023, to $947.84 million, with most of them imported from Poland (almost 20%).

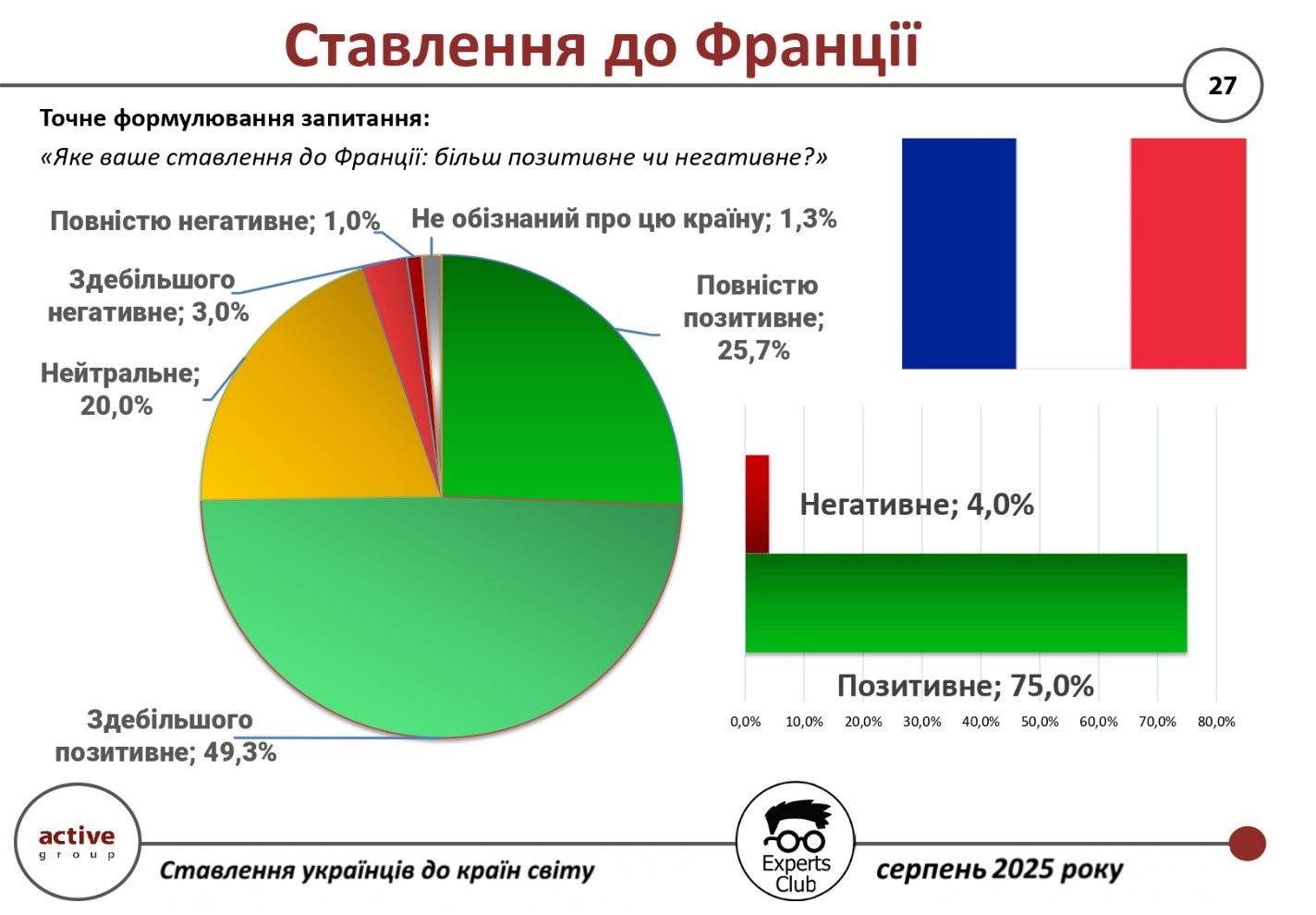
The level of sympathy for France among Ukrainians remains high. This is evidenced by the results of an all-Ukrainian sociological survey conducted by Active Group in cooperation with the Experts Club information and analytical center in August 2025.
According to the survey, 75.0% of Ukrainian citizens have a positive attitude toward France (49.3% are mostly positive, 25.7% are completely positive). Only 4.0% of respondents have a negative perception of this country (3 . 0% – mostly negative, 1.0% – completely negative). Another 20.0% remain neutral, and 1.3% said they do not have enough information about France.
“For many Ukrainians, France is a symbol of support in difficult times, as well as a cultural and political reference point in Europe. Such indicators demonstrate high trust and respect, which is largely due to the active role of Paris in European policy towards Ukraine,” said Oleksandr Poznyi, co-founder of Active Group.
In his turn, Maxim Urakin, founder of Experts Club, emphasized the importance of France in economic cooperation.
“In the first half of 2025, the trade turnover between Ukraine and France amounted to more than $1.37 billion. At the same time, exports of Ukrainian goods amounted to only $395.6 million, while imports from France reached $979.4 million. The negative balance of more than $583 million indicates a significant dependence of our market on French goods, but also the importance of France as an economic partner,” he said.
The survey is part of a broader research program that analyzes international sympathies and antipathies of Ukrainians in the current geopolitical context.
The full video can be viewed here:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YgC9TPnMoMI&t
You can subscribe to the Experts Club YouTube channel here:
https://www.youtube.com/@ExpertsClub
ACTIVE GROUP, DIPLOMACY, EXPERTS CLUB, FRANCE, Poznyi, SOCIOLOGY, TRADE, URAKIN

Denmark and Germany have agreed to participate in the new format of arms supplies to Kyiv proposed by US President Donald Trump, while France, Italy, the Czech Republic, and Hungary have refused, Western media reported on Wednesday.
In addition, Bloomberg reported on Wednesday that Europe increasingly feels the need to end its dependence on US weapons.
“Europe is heavily dependent on the US defense industry. However, due to trade tariffs, President Trump’s attitude toward NATO and his lack of commitment to defending the alliance’s countries, European countries will increasingly prioritize investments in their own defense systems,” the agency’s sources said.
According to the European portal Politico, France has refused to participate in the purchase of American weapons for Ukraine. The publication’s sources said that instead, the government intends to focus on increasing its own defense budget, which President Emmanuel Macron promised last weekend to almost double by 2027 compared to the 2017 budget.
In addition, Paris wants to support European manufacturers who previously supplied Ukraine with anti-missile systems and other weapons.
Italy also has no plans to purchase weapons from the US for delivery to Ukraine, but will continue to provide military assistance to Kyiv. Unnamed representatives of the Ministry of Defense told the newspaper La Stampa that there had never been any talks about purchasing American weapons for Kyiv.
In addition, the newspaper notes that Italy does not have the funds to carry out operations of this kind. According to the newspaper’s sources, the problem is so acute that the only purchase from the US planned by Italy for the next ten years is a batch of F-35 fighter jets for its own needs.
The Czech government, in turn, said that military aid to Kyiv would continue, but through participation in other initiatives and purchases from Czech, not American, manufacturers.
Hungarian Foreign Minister Péter Szijjártó said that Budapest does not intend to participate in the purchase of American weapons for Ukraine.
Berlin and Copenhagen have so far given their official consent to purchase weapons from the US. Danish Foreign Minister Lars Rasmussen said he was fully prepared to join the funding.
The Dutch Foreign Ministry, in turn, said it was considering participating in the program. However, despite the government’s positive assessment of the initiative, Amsterdam has not yet confirmed its commitment to direct participation.
According to NATO Secretary General Mark Rutte, Sweden, Norway, and the United Kingdom are also expected to join the funding.
On July 11, Trump announced that US NATO allies would purchase weapons from Washington, which could then be transferred to Ukraine.
During a press conference with Trump on Monday, Rutte called it “logical” that European countries would pay for US arms deliveries to Ukraine.
European diplomacy chief Kaja Kallas said on Tuesday that EU countries would prefer Washington to provide part of its military aid to Ukraine free of charge. “If we pay for these weapons, it means that we, not the US, are providing this military aid,” Callas said at a press conference in Brussels. She stressed that Brussels “would like to see these costs shared.”