
Electricity imports to Ukraine in January 2026 increased by 40% compared to December 2025 and amounted to 894.5 thousand MWh, according to the DIXI Group analytical center, citing data from Energy Map.
“This is the highest monthly figure since the launch of the new electricity market in July 2019,” the center said.
There were no electricity exports in January.
For comparison: in January 2025, electricity imports amounted to 183.1 thousand MWh, while exports amounted to 84.7 thousand MWh, according to statistics from DIXI Group.
In January, Hungary accounted for the largest share of imports – 45%, or 402.0 thousand MWh. Romania accounted for 21% of the resources provided to Ukraine (185.9 thousand MWh), Slovakia – 18% (159.8 thousand MWh), Poland – 15% (135.2 thousand MWh), and Moldova – 1% (11.6 thousand MWh).
The growth in imports from European countries ranged from 18% to 62%, with the exception of Moldova, from which supplies decreased by 18%.
According to DIXI Group analysts, in January 2026, the maximum capacity of inter-state crossings for electricity imports from the European Union to the joint Ukraine-Moldova regulation block increased to 2.45 thousand MW, which is a record since Ukraine joined the ENTSO-E network. At the same time, part of this capacity is used to import electricity to Moldova, so Ukraine has access to about 2.1 thousand MW of commercial imports. At the same time, the amount of permitted import capacity for each of the countries in the block is dynamic and may change depending on the operational situation in the countries’ power systems.
On average, during January, the use of available transmission capacity was 57.3% of the accepted nominal value (2.1 GW). The maximum level of utilization was recorded on January 24 between 16:00 and 17:00, at 104%, while the minimum was recorded on January 9 during the same time interval (19.9%).
“Thus, Ukraine ended January 2026 as a net importer of electricity, which was the fourth consecutive month that the country remained in this status and reflects the critical role of imports in maintaining the stability of the power system in the face of massive attacks and high seasonal consumption,” DIXI Group emphasized.
Analysts at the center recalled that during January, Ukraine’s energy system operated under increased load, and on January 16, a state of emergency was declared in the country’s energy sector. In January, Russia used more than 6,000 strike drones, about 5,500 guided aerial bombs, and 158 missiles of various types against Ukraine’s energy system and critical infrastructure. In total, Russia carried out six massive strikes during the month, damaging power generation facilities as well as electricity transmission and distribution networks. The attacks took place against the backdrop of significantly worsening weather conditions and lower air temperatures, which further increased the load on the system.
One of the factors contributing to the increase in electricity imports was the rise in price caps in the short-term market segments.
As reported, the National Commission for State Regulation of Energy and Public Utilities (NKREKP) at an extraordinary meeting on January 16, set the maximum price limit for electricity on the day-ahead market (DAM) and intraday market (IDM) at UAH 15,000/MWh for the entire day for the period from January 18 to March 31, 2026.
The NEURC made this decision after statements by First Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of Energy of Ukraine Denys Shmyhal regarding the government’s expectations from the regulator to review the maximum prices for electricity on the spot market and to equalize the day and night price caps in order to attract electricity imports throughout the day.
After the adoption of this decision, the BASE electricity price index for the Ukrainian DAM reached a record high of 13,232.96 UAH/MWh at the auction on January 22, which is 1.8 times higher than the average value of this indicator for the 20 days of January – 7,307.04 UAH/MWh.
According to ENTSOE data, in January 2026, Ukraine ranked first in terms of the average daily BASE price index on the DAM 14 times (January 2-4, 10-11, 16-17, 19, 21, 23-25, 27-28), compared to 26 European countries.
At the end of 2025, Ukraine ranked second among 27 European countries in terms of the BASE index on the DAM, which amounted to 5,292.62 UAH/MWh, calculated according to Central European Time (CET).

The share of imported cheeses on the Ukrainian market in 2025 has grown from 38% to 45% and continues to increase. If the situation does not change, Ukrainian producers will have less than half of the market by March-April 2026, according to the Ukrainian Dairy Industry Association (UDIA).
“The current trend in the cheese market poses a threat to Ukraine’s food security and requires an immediate response from the government. If, for political reasons, anti-subsidy investigations against EU producers, primarily Poland, have no prospects, it is worth focusing on intensifying state support for Ukrainian producers,” said Arsen Didur, executive director of the UDAU.
The industry association noted that imports of rennet cheese to Ukraine last year increased by 13% compared to 2024, to 32.9 thousand tons, in particular, 15.8 thousand tons (+14%) of hard cheese were imported.
The SMU sent a proposal to the government to increase compensation under the National Cashback program for Ukrainian-produced cheese from 10% to 20%. At the same time, it is proposed to reduce or cancel compensation for other dairy products that do not face such fierce competition from imports.
As reported, Minister of Economy, Environment, and Agriculture Oleksiy Sobolev announced in January that in 2026, the Cabinet of Ministers would reduce funding for the National Cashback program. As of February 2026, the state budget allocates UAH 3 billion for this program, compared to UAH 5.7 billion a year ago. Therefore, the government plans to move to targeted support for critically important industries.

In 2025, Ukraine imported 93.2% more cabbage than a year earlier, amounting to 48.41 thousand tons, while procurement costs increased by 86.1% to $44.90 million, according to the State Customs Service.
The main suppliers of cabbage were North Macedonia (31.29%), Poland (24.05%), and the Netherlands (13.79%).

In 2025, Ukraine imported 123,600 tons of potatoes, which is 2.4 times more than in 2024; the cost of purchasing them increased 2.5 times to $66.29 million, according to the State Customs Service.
Poland (37.1%), Egypt (13.56%), and the Netherlands (11.58%) became the leaders in potato supplies to Ukraine.

In 2025, Ukraine imported 12.85 thousand tons of cut flowers, which is 8.5% more than in 2024 (11.84 thousand tons), according to the State Customs Service.
According to the published statistics, in monetary terms, the volume of imports last year increased by 14.2% to $64.48 million, compared to $56.46 million a year ago.
The Netherlands remains the undisputed leader in supplies, providing almost three-quarters of the Ukrainian market, or 72.4% of supplies in monetary terms, or $46.68 million. Ecuador (12.8%, or $8.25 million) and Kenya (6.2%, or $4.00 million) also lead in flower supplies to Ukraine. In 2024, this trio remained the same with similar shares of supplies: the Netherlands (71.1%), Ecuador (13.5%), and Kenya (5.8%).
Flower exports from Ukraine in 2025 remained symbolic, amounting to only $184,000 at the end of the year, which is 12.5% less than in 2024 ($210,000). The main buyers of Ukrainian flowers were Moldova (59% or $108,600), Georgia (23% or $42,300), and Lithuania (10% or $18,400). A year ago, the composition of the top three buyers was slightly different: Moldova was also the leader (58% or $121,800), but it was followed by Poland (17% or $35,700) and Lithuania (12% or $25,200).
As reported, in 2021, Ukraine introduced a special three-year duty on imports of cut fresh roses, regardless of the country of origin and export. The duty rate in the first year of its application was 56%, in the second — 44.8%, and in the third — 35.84%.
Based on the results of the duty’s impact provided by the Ministry of Economy, the Interdepartmental Commission on International Trade (ICIT) concluded in 2025 that the application of special measures had a positive effect on the activities of domestic producers, but did not completely eliminate the consequences of the damage caused to them. Recommendations to extend the duty were forwarded to the ministry.

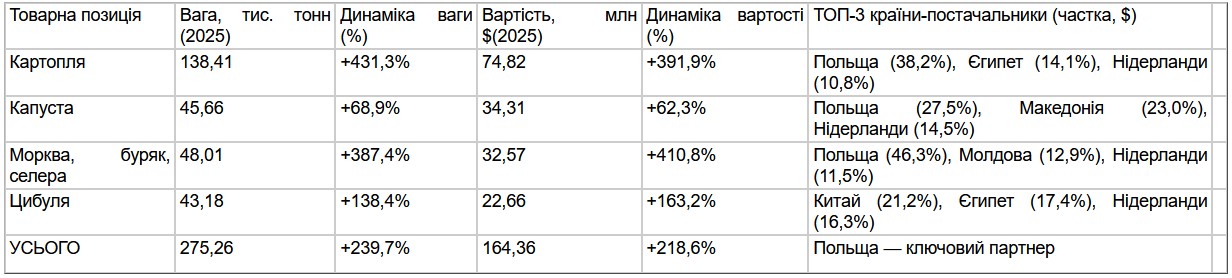
In 2025, Ukraine imported $89.54 million worth of vegetables used in borscht, including carrots, beets, cabbage, and onions, and $164.36 million worth of potatoes.
According to statistics released by the State Customs Service (SCS), Ukraine increased its imports of onions by 2.4 times in 2025, to 43,180 tons. The purchase cost $22.66 million, which is 2.6 times more than the $8.61 million spent in 2024. The top three suppliers of onions to Ukraine were China and Egypt, which accounted for 21.2% and 17.44% of imports, amounting to $4.80 million and $3.95 million, respectively. The Netherlands rounded out the top three with a 16.33% share ($3.70 million).
During this period, Ukraine imported 68.9% more cabbage than last year — 45.66 thousand tons versus 27.03 thousand tons, respectively. The cost of purchasing it increased by 62.3% and amounted to $34.31 million (compared to $21.14 million in 2024). The main suppliers were Poland (27.45% of supplies worth $9.42 million), Macedonia (22.96% worth $7.88 million), and the Netherlands (14.48% worth $4.97 million).
Ukraine increased its imports of carrots, beets, and celery by 4.9 times in 2025, to 48,010 tons (compared to 9,850 tons in 2024). USD 32.57 million was spent on these needs, which is 5.1 times more than in 2024 (USD 6.37 million). Last year, the main suppliers of these root vegetables to Ukraine were Poland, Moldova, and the Netherlands, which accounted for 46.31%, 12.9%, and 11.54% of the imported volume, respectively. In monetary terms, they earned $15.08 million, $4.20 million, and $3.76 million from these supplies, respectively.
As reported, Ukraine imported 138.41 thousand tons of potatoes in 2025, which is 5.3 times more than in 2024. In monetary terms, potato imports increased 4.9 times, to $74.82 million, compared to $15.21 million a year ago.
In total, Ukraine imported 275.26 thousand tons of vegetables for borscht in 2025.
Imports of vegetables for borscht to Ukraine (2025 vs. 2024)
Data: State Customs Service