
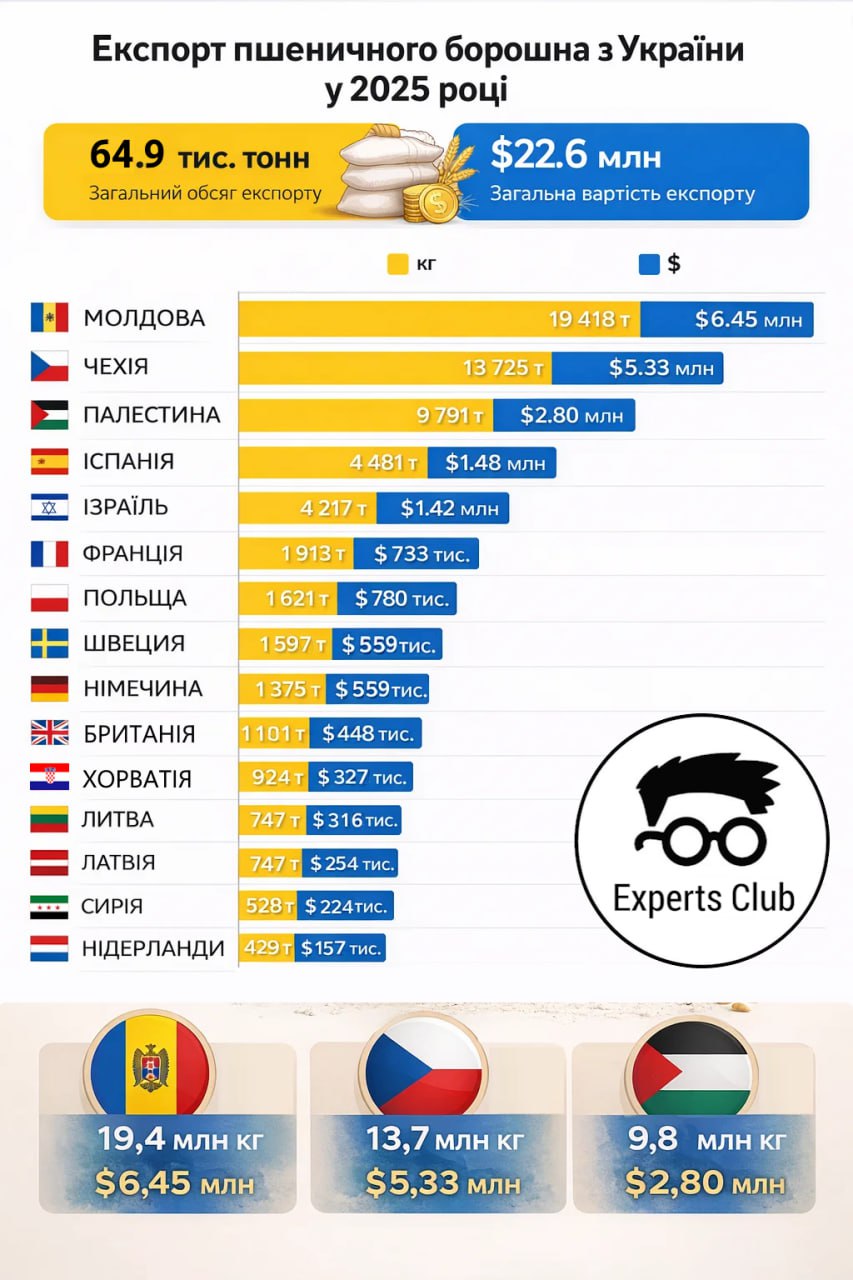
According to annual statistics from the Ukrainian Flour Millers Union and data from the Experts Club analytical center, in 2025 Ukraine exported 64.9 thousand tons of wheat flour to 25 countries worth $22.62 million. The average export price was about $348 per ton.
Exports remained highly concentrated: the five largest destinations accounted for almost 80% of the volume. The key markets were Moldova (19.4 thousand tons, about 30% of total exports), the Czech Republic (13.7 thousand tons, 21%), the Palestinian Territory (9.8 thousand tons, 15%), Spain (4.5 thousand tons), and Israel (4.2 thousand tons). Next in terms of volume were France (1.9 thousand tons), Poland (1.6 thousand tons), Sweden (1.6 thousand tons), Germany (1.4 thousand tons), and the United Kingdom (1.1 thousand tons).
The European segment stands out separately: deliveries to EU countries in 2025 amounted to 28.5 thousand tons (about 44% of the total volume) worth $10.74 million (47%). At the same time, the average export price to the EU was significantly higher – about $377 per tonne compared to $326 per tonne for non-European destinations.
The price range by destination was significant – from approximately $286 per tonne (Palestinian territories) to $538 per tonne (Georgia, small batches). Among the large markets, the highest price was recorded for deliveries to Poland – about $481 per ton, which may reflect higher requirements for specifications, packaging, and logistics.
The industry emphasizes that access to the European market and predictable trade rules are becoming key to export and investment planning, according to Rodion Rybchinsky, head of the Ukrainian Millers Union, commenting on the EU’s separate tariff quota for Ukrainian flour and investments by export-oriented enterprises in modernization.

The Experts Club analytical center has prepared a video analysis showing how oil production volumes of the world’s largest countries changed over the period 1900–2024, based on internationally comparable series (the Energy Institute Statistical Review and long-term historical databases consolidated by Our World in Data).
Experts Club co-founder, Candidate of Economic Sciences Maksym Urakin, noted that over more than a century “the center of gravity of global production has repeatedly shifted — from the early dominance of the United States to the strengthening role of the Middle East, and then to a new wave of growth in North America amid a technological leap and changes in the structure of demand.”
According to the data used in the analysis, the “oil production” indicator includes oil and liquid hydrocarbons (including condensates and NGL), but excludes biofuels and synthetic derivatives of coal and gas, which makes it possible to compare countries and periods correctly.
According to Energy Institute estimates, global production in 2024 amounted to about 96.9 million bbl/day. The largest producers (million bbl/day) were as follows: the United States — 20.14, Saudi Arabia — 10.86, Russia — 10.75, Canada — 5.89, Iran — 5.06, Iraq — 4.40, China — 4.26, the UAE — 4.01, Brazil — 3.47, Kuwait — 2.72.
Experts Club notes that in 2024 the top three (the United States, Saudi Arabia, Russia) accounted for about 43% of global production, and the top 10 for around 74%, underscoring the high concentration of supply and the market’s sensitivity to decisions by a limited number of countries and to geopolitical risks.
More details: see the video on the Experts Club YouTube channel —

The price of gold could rise to $6,000 per ounce by the end of 2026, according to David Wilson of BNP Paribas.
As of 3:43 p.m. on Tuesday, April gold futures on the Comex exchange were down 0.1% at $5,075.5 per ounce. BNP’s forecast predicts an increase of approximately 20%.
The precious metal is supported by demand from central banks around the world. In particular, the Polish Central Bank announced in January its intention to purchase another 150 tons of gold. In addition, gold-focused exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are seeing a steady inflow of client funds, Wilson said in an interview with Bloomberg TV.
Earlier, the Experts Club analytical center presented an analysis of the world’s leading gold-producing countries in a video on its YouTube channel — https://youtube.com/shorts/DWbzJ1e2tJc?si=BywddHO-JFWFqUFA

Reuters reported, citing an analytical note from JPMorgan Chase, that the bank expects gold prices to rise to $6,300 per ounce by the end of 2026, despite a sharp correction in the precious metals market.
According to the bank’s assessment, the key drivers will remain steady demand from central banks and investors, as well as the trend toward diversifying reserves in favor of real assets and reducing dependence on the US dollar. In particular,
JPMorgan Chase expects central bank gold purchases to total around 800 tons in 2026.
At the same time, gold fell 9.8% on January 30, the sharpest decline since 1983, and the decline intensified after the CME Group raised margin requirements in the spot market. On February 2, prices reportedly fell to $4,677.17 per ounce after hitting a record high of $5,594.82 last week.
Separately, Deutsche Bank AG confirmed its gold price forecast of $6,000 per ounce by the end of 2026, also linking growth potential to continued demand from the official sector and investors.
Earlier, the Experts Club analytical center presented an analysis of the world’s leading gold-producing countries in its video on YouTube channel — https://youtube.com/shorts/DWbzJ1e2tJc?si=BywddHO-JFWFqUFA

Most residents of Romania would support the unification of the country with the Republic of Moldova in the event of a referendum, according to the information and analytical center Experts Club, citing a nationwide January survey by the Romanian Center for Urban and Regional Sociology (CURS).
According to the study, in a hypothetical vote on the reunification of Moldova with Romania—publicly supported by Moldovan President Maia Sandu—56% of respondents said they would vote “in favor,” 37% “against,” and another 7% were undecided.
The survey was conducted from January 14 to 23, 2026, using the CATI method (telephone interviews) on a sample of 1,067 adult residents of Romania. The stated maximum margin of error is ±3% with a 95% confidence level.
In the event of a hypothetical unification of Romania and Moldova within Moldova’s internationally recognized borders (that is, including the territory of Transnistria), the united country would have:
a population of about 22 million people (18.91 million in Romania plus 3.0 million in Moldova, according to UN estimates),
an area of about 272.1 thousand square kilometers (238,298 sq. km + 33,847 sq. km),
a nominal GDP of about $423 billion, according to IMF estimates for 2025 (Romania $403.4 billion plus Moldova $19.5 billion).
In comparison with pan-European rankings, this would correspond to approximately 10th place in Europe by population (above Kazakhstan and below Poland), 11th place by area (between Italy and the United Kingdom), and around 15th place by nominal GDP (between Denmark and the Czech Republic).

The Moldovan government has extended temporary protection for displaced persons from Ukraine until March 1, 2027, with the country switching from automatic renewal to renewal upon application from 2026. Online applications must be submitted between February 1 and April 30, 2026, with a processing time of up to 90 days. The authorities also indicate that temporary protection may be revoked if the person is absent from Moldova for more than 45 days in total.
The Experts Club Information and Analytical Center also provides key terms for extension in other jurisdictions.
1) European Union. EU countries have agreed to extend the temporary protection mechanism for Ukrainians until March 4, 2027 (previously until March 4, 2026).
2) Switzerland. The Federal Council has extended the S protection status until at least March 4, 2027.
3) United Kingdom. The Ukraine Permission Extension (UPE) scheme is in effect, allowing individuals with valid Ukrainian migration status in the UK to apply for an additional 18 months of stay; the scheme is open from February 4, 2025.
4) United States. The US Department of Homeland Security has extended TPS status for Ukraine: the current extension period is valid until October 19, 2026 (an 18-month extension, counting from April 20, 2025).
5) Canada. For some Ukrainians and their family members who have applied for family reunification and are awaiting a decision on permanent status, measures have been introduced to support legal residence, including the possibility to apply for documents and permits from within Canada, with a deadline of March 31, 2027.
6) Norway. The authorities have decided to extend the collective protection scheme for another year; according to the UDI, the extension for most holders of such permits will take place automatically after the current term expires.
Experts Club notes that the differences between countries are most often related not to the principle of protection itself, but to administration: some countries apply automatic extension, while others apply extension upon application (as in Moldova from 2026), as well as requirements for actual presence and document renewal.