
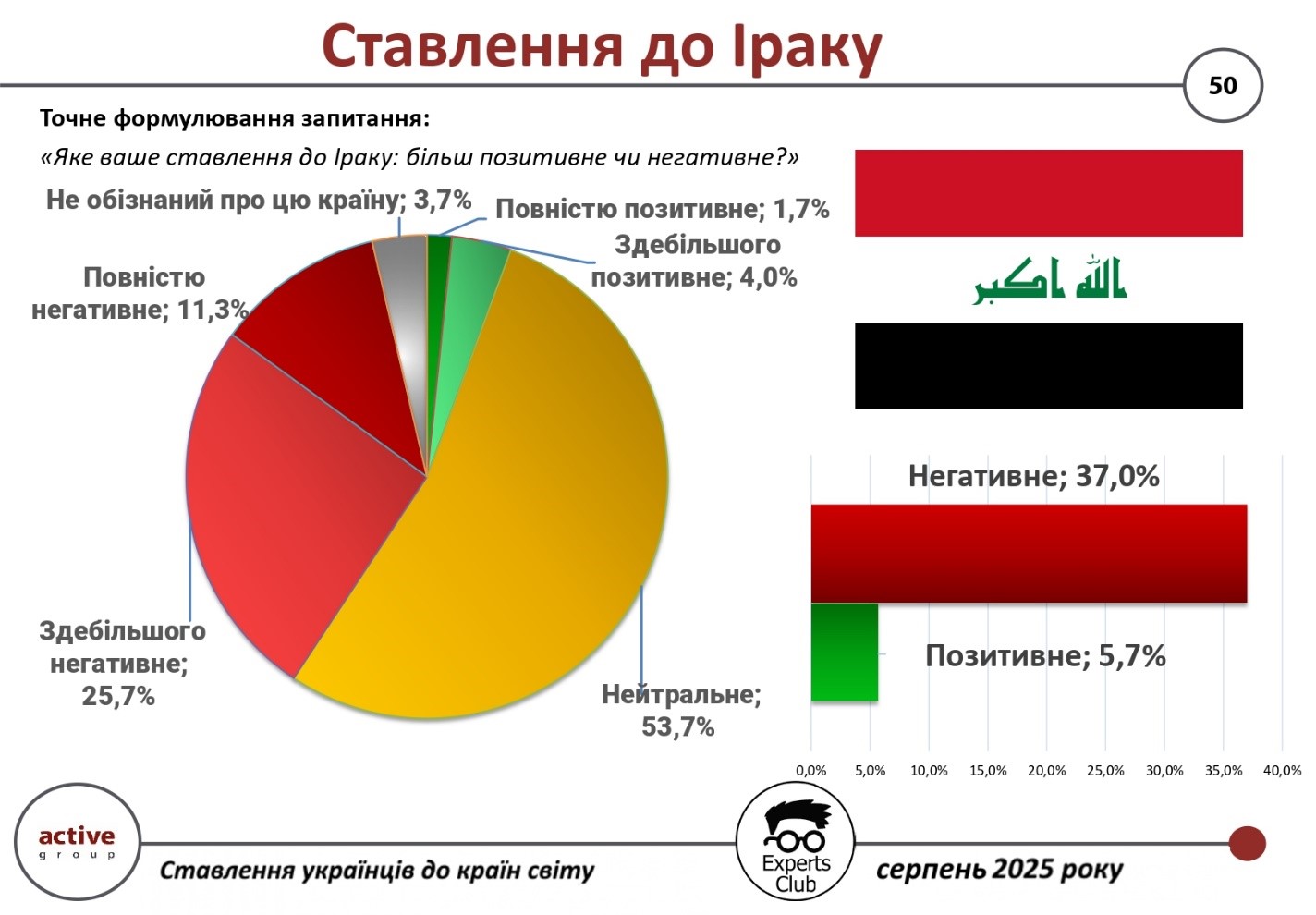
More than half of Ukrainians express a neutral attitude toward Iraq, but at the same time, a significant proportion of respondents rated the country negatively. This is evidenced by the results of a survey conducted by Active Group in cooperation with the Experts Club think tank.
According to the study, 53.7% of respondents said their attitude toward Iraq is neutral. At the same time, 37.0% said they have a negative attitude (11.3% — completely negative, 25.7% — mostly negative). Only 5.7% of Ukrainians expressed positive views (1.7% — completely positive, 4.0% — mostly positive). Another 3.7% of respondents said they were not familiar with the country.
“Ukrainians associate Iraq primarily with wars, instability, and crises, which significantly affects their perception of the country. At the same time, more than half of the respondents demonstrate a neutral position, which indicates the absence of a clear personal assessment,” commented Alexander Pozniy, head of Active Group.
Maksim Urakin, co-founder of Experts Club, emphasized the specifics of economic relations.
“Despite the fact that some of our fellow citizens may confuse Iran and Iraq, the latter is one of our most profitable trading partners. Ukraine’s trade turnover with Iraq in January-August 2025 amounted to $189.3 million. At the same time, exports from Ukraine amounted to $189.2 million, while imports amounted to only $0.16 million. This structure creates a significant positive balance of over $189 million, making Iraq primarily a market for Ukrainian products rather than a source of imports,” Urakin emphasized.
Thus, Ukrainians’ attitude toward Iraq remains neutral overall, with a high proportion of negative assessments, while economic relations are one-sided and focused on Ukrainian exports.
The full video can be viewed at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YgC9TPnMoMI&t
You can subscribe to the Experts Club YouTube channel here: https://www.youtube.com/@ExpertsClub
ACTIVE GROUP, EXPERTS CLUB, IRAQ, Pozniy, SOCIOLOGY, TRADE, UKRAINE, URAKIN

Most Ukrainians take a neutral stance toward Serbia, but among those who expressed a clear opinion, negative assessments outweigh positive ones. This is evidenced by the results of a survey conducted by Active Group in cooperation with the Experts Club think tank.
According to the study, 58.0% of respondents said they had a neutral attitude toward Serbia. At the same time, 26.0% of Ukrainians expressed a negative attitude (4.7% — completely negative, 21.3% — mostly negative). Only 13.7% of respondents gave positive assessments (2.3% — completely positive, 11.3% — mostly positive). Another 2.3% said they were not familiar with the country.
“Serbia remains a country with an ambiguous image for Ukrainians. Despite historical and cultural ties, Belgrade’s political positions shape a predominantly negative attitude among part of Ukrainian society,” said Alexander Pozniy, head of Active Group.

Maksym Urakyn, founder of Experts Club, emphasized that trade and economic relations between Ukraine and Serbia are developing at a moderate pace.
“In January-August 2025, trade turnover between the countries amounted to $220.6 million. At the same time, exports from Ukraine to Serbia amounted to $85.1 million, and imports from Serbia amounted to $135.5 million. The negative balance for Ukraine is $50.4 million. This small trade balance is quite insignificant and does not reflect the potential of the countries.”
Thus, although most Ukrainians do not have a clear position on Serbia, the balance of assessments is rather negative.
The full video can be viewed at the link:
You can subscribe to the Experts Club YouTube channel here:
ACTIVE GROUP, EXPERTS CLUB, Pozniy, SERBIA, SOCIOLOGY, TRADE, UKRAINE, URACIN

Experts Club has released a video analysis dedicated to the dynamics of gold production in the world by leading countries. Over the past half-century, the structure of global gold production has changed significantly: while South Africa and the USSR were the leaders in the 1970s, by the 2020s, China, Australia, and Russia had taken the lead.
China is now the largest gold producer in the world, having led the field by a significant margin for almost 20 years. Russia is in second place, Australia in third.
Further down the top ten are Canada, the US, Ghana, Mexico, Indonesia, Peru, and Uzbekistan.
In the 1970s and 1990s, South Africa dominated, accounting for up to two-thirds of global gold production. The gradual depletion of deposits and rising costs led to a decline in its share. South Africa has now fallen out of the top ten countries in terms of gold production.
In the 1990s, Russia took the lead, and in the last two decades, there has been significant growth in gold production in Australia, Canada, and African countries (Ghana, Mali).
Total global gold production has more than doubled since 1975, exceeding 3,600 tons per year by 2023–2024.
Since the early 2020s, gold has been steadily updating its historical highs amid geopolitical instability and inflationary risks. As of September 2025, the price of gold reached about $3,710-$3,730/ounce. This rapid rise in price is supported by increased demand from central banks, investment flows into ETFs, and expectations of lower interest rates in the US.
For more details on the struggle between countries for global leadership in gold production, see the video from Experts Club – https://www.youtube.com/shorts/DWbzJ1e2tJc
“Gold is not only used in the jewelry industry and finance, but also in electronics (coating contacts and connectors, where high conductivity and corrosion resistance are important), modern computers and smartphones are impossible without the use of gold. Gold is used in aviation and space technology, medicine, and lasers. Gold is also used as a catalyst in chemical reactions (for example, in the production of certain types of fuel),” commented Maxim Urakin, candidate of economic sciences and co-founder of the Experts Club information and analytical center, in the video.
The rise in prices confirms the importance of gold as a “safe haven” in times of global turbulence.

Почти половина украинцев выражает положительное отношение к Казахстану, тогда как отрицательные оценки остаются относительно немногочисленными. Об этом свидетельствуют результаты опроса, проведенного компанией Active Group совместно с аналитическим центром Experts Club.
Согласно исследованию, 42,7% респондентов имеют положительное отношение к Казахстану (8,7% — полностью положительное, 34,0% — в основном положительное). При этом 48,7% заняли нейтральную позицию. Негативно высказались только 8,0% опрошенных (1,7% — полностью негативно, 6,3% — в основном негативно). Только 0,7% отметили, что не знакомы с этой страной.

«Казахстан для украинцев является партнером в постсоветском пространстве, который воспринимается скорее нейтрально или умеренно положительно. Существенного негатива в отношении населения нет», — прокомментировал результаты исследования руководитель компании Active Group Александр Позний.
Экономические показатели подтверждают взаимовыгодность сотрудничества. Как подчеркнул соучредитель Experts Club Максим Уракин, в январе-августе 2025 года товарооборот между Украиной и Казахстаном составил 202,0 млн долларов США.
«Украинский экспорт в Казахстан достиг 157,8 млн долларов, тогда как импорт — 44,2 млн долларов. Положительное сальдо для Украины составляет более 113,5 млн долларов, что свидетельствует о чрезвычайно выгодном балансе в двусторонней торговле», — подчеркнул эксперт.
Таким образом, Казахстан воспринимается украинцами как страна с относительно положительным имиджем и важным торговым партнером Украины.
Полное видео можно посмотреть по ссылке:
Подписаться на YouTube-канал Experts Club можно здесь:
ACTIVE GROUP, EXPERTS CLUB, КАЗАХСТАН, Позний, СОЦИОЛОГИЯ, ТОРГОВЛЯ, УКРАИНА

Almost half of Ukrainians express a positive attitude toward Kazakhstan, while negative assessments remain relatively few. This is evidenced by the results of a survey conducted by Active Group in collaboration with the Experts Club analytical center.
According to the study, 42.7% of respondents have a positive attitude towards Kazakhstan (8.7% — completely positive, 34.0% — mostly positive). At the same time, 48.7% took a neutral position. Only 8.0% of respondents expressed a negative opinion (1.7% — completely negative, 6.3% — mostly negative). Only 0.7% said they were not familiar with the country.

“For Ukrainians, Kazakhstan is a partner in the post-Soviet space that is perceived as neutral or moderately positive. There is no significant negativity in the attitude of the population,” commented Alexander Pozniy, head of Active Group, on the results of the study.
Economic indicators confirm the mutual benefits of cooperation. As Maxim Urakin, co-founder of Experts Club, pointed out, in January–August 2025, trade turnover between Ukraine and Kazakhstan amounted to $202.0 million.
“Ukrainian exports to Kazakhstan reached $157.8 million, while imports amounted to $44.2 million. The positive balance for Ukraine is over $113.5 million, which indicates an extremely favorable balance in bilateral trade,” the expert emphasized.
Thus, Kazakhstan is perceived by Ukrainians as a country with a relatively positive image and an important trading partner of Ukraine.
The full video can be viewed at:
You can subscribe to the Experts Club YouTube channel here:
ACTIVE GROUP, EXPERTS CLUB, KAZAKHSTAN, Pozniy, SOCIOLOGY, TRADE, UKRAINE, URIKIN

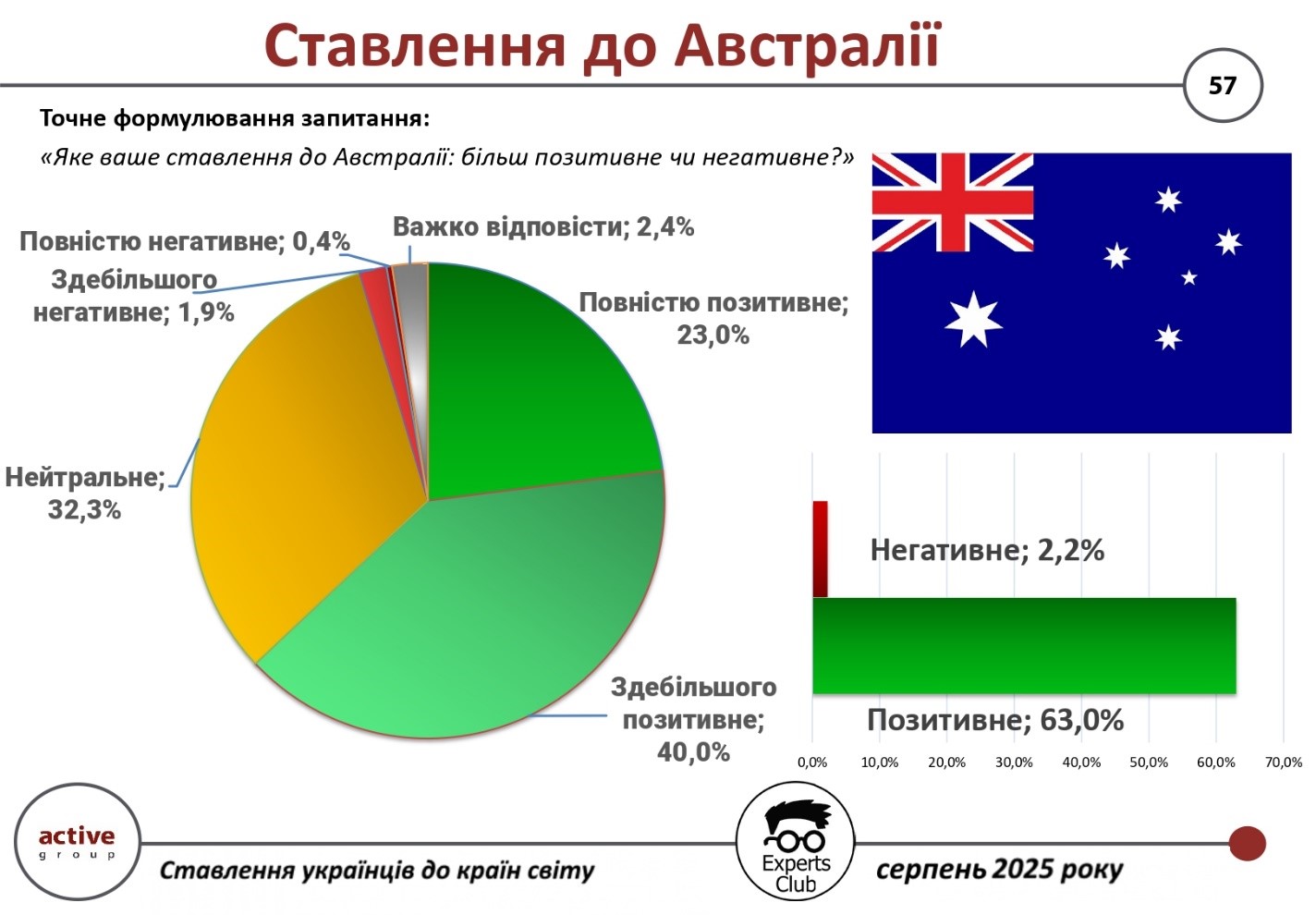
According to the results of a study conducted by Active Group in collaboration with Experts Club in August 2025, Ukrainians’ attitude towards Australia is predominantly positive. 63.0% of respondents expressed a positive attitude towards this country, while only 2.2% of respondents had a negative attitude. At the same time, 32.3% took a neutral position, and 2.4% admitted that they found it difficult to answer this question.
The largest share of positive responses fell into the “mostly positive” category – 40.0%, while 23.0% of respondents expressed a “completely positive” attitude. On the other hand, 1.9% of respondents had a “mostly negative” attitude, and only 0.4% had a “completely negative” attitude.
In 2024, trade turnover between Ukraine and Australia amounted to US$157.4 million. At the same time, exports of Ukrainian goods to Australia amounted to only US$6.4 million, while imports of Australian products amounted to US$151.0 million. The negative balance for Ukraine was recorded at US$144.6 million.
“The main areas of Australian exports to Ukraine traditionally include mineral raw materials, industrial goods, and agricultural products. In contrast, Ukrainian exports to Australia have a limited range and are mainly concentrated in the agricultural and metallurgical sectors,” notes economist and founder of Experts Club Maksim Urakin.
The full video can be viewed at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YgC9TPnMoMI&t
You can subscribe to the Experts Club YouTube channel here: https://www.youtube.com/@ExpertsClub
ACTIVE GROUP, AUSTRALIA, EXPERTS CLUB, Pozniy, SOCIOLOGY, TRADE, UKRAINE, URAKIN