
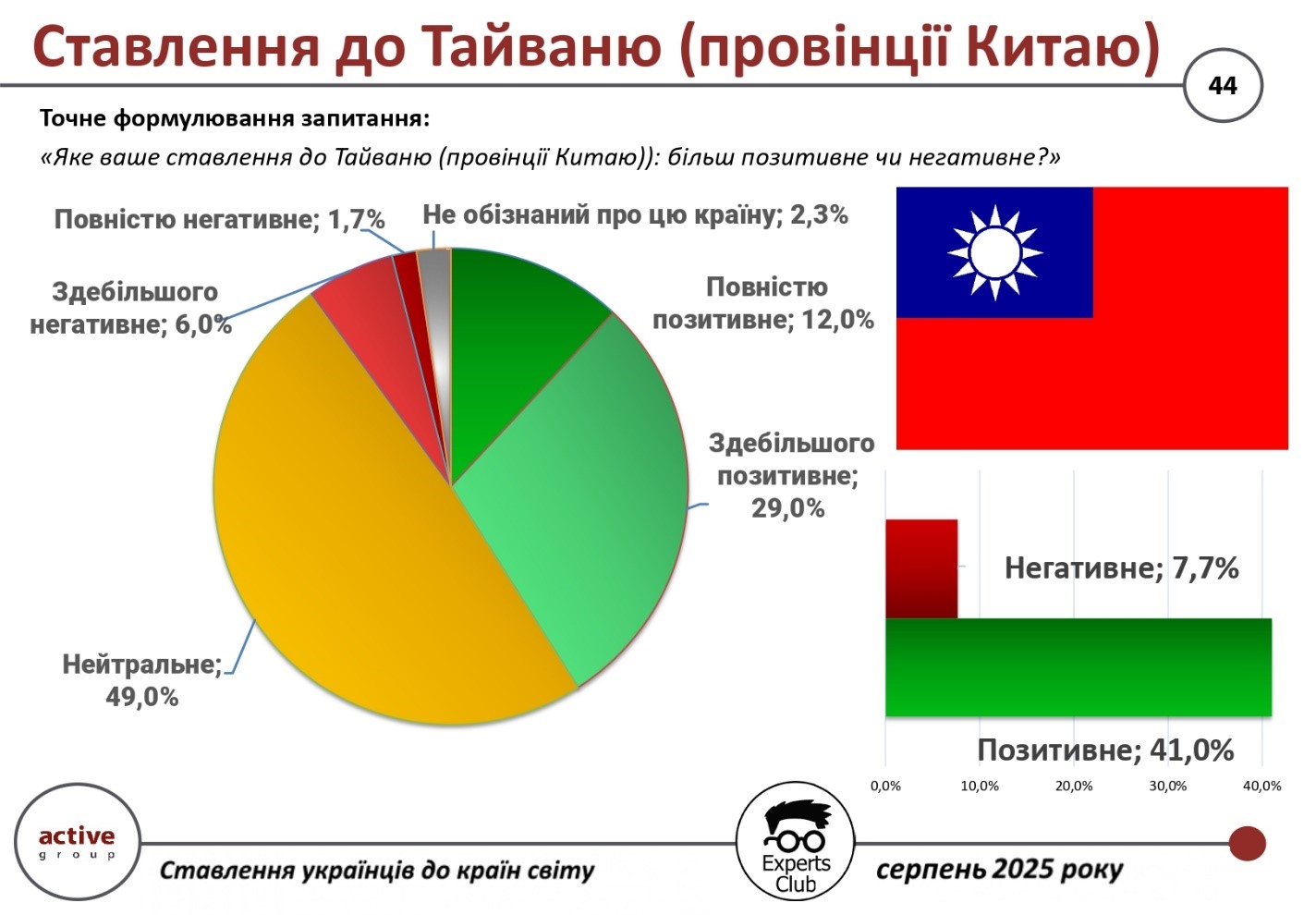
The results of a study conducted by Active Group and Experts Club in August 2025 showed that Ukrainians generally have a favorable attitude toward Taiwan, although a significant portion of respondents remain neutral.
Thus, 41.0% of respondents expressed a positive attitude (12.0% – completely positive, 29.0% – mostly positive). Only 7.7% gave negative assessments, while almost half — 49.0% — took a neutral position, and 2.3% admitted to being insufficiently informed about this country.
“Taiwan is perceived quite evenly in Ukrainian society, without any strong emotions. At the same time, the positive significantly outweighs the negative, which indicates the general open attitude of Ukrainians towards this important player in the global economy,” said Alexander Pozniy, head of Active Group.
Maksim Urakin, founder of Experts Club, noted that there is a significant imbalance in trade and economic relations between Ukraine and Taiwan:
“According to the results of January-August 2025, trade turnover amounted to about $262.1 million. At the same time, exports from Ukraine amounted to only $8.8 million, while imports from Taiwan amounted to more than $253.3 million. As a result, the negative balance exceeded $244.6 million. This indicates the weak representation of Ukrainian goods on the Taiwanese market,” he said.
Thus, Taiwan occupies an important place in Ukraine’s foreign economic relations, but mainly as a supplier of high-tech goods.
The full video can be viewed at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YgC9TPnMoMI&t
You can subscribe to the Experts Club YouTube channel here: https://www.youtube.com/@ExpertsClub
ACTIVE GROUP, ASIA, EXPERTS CLUB, Pozniy, SOCIOLOGY, TAIWAN, TRADE, UKRAINE, УРАКИН

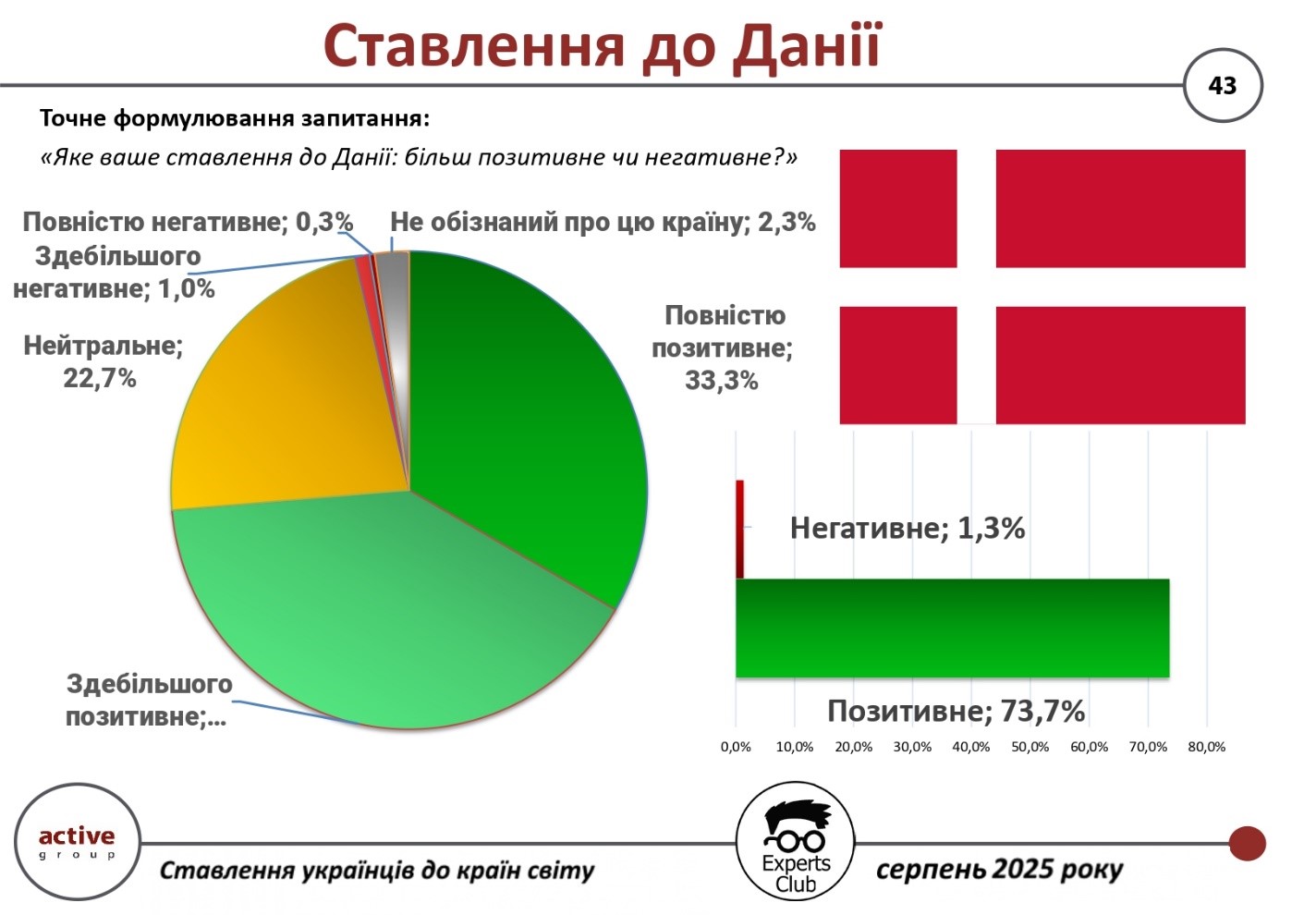
The results of a survey conducted by Active Group and Experts Club in August 2025 show that Ukrainians have a very favorable attitude towards Denmark.
Thus, 73.7% of respondents expressed a positive attitude (33.3% — completely positive, 40.3% — mostly positive). Only 1.3% of respondents gave negative assessments, while 22.7% took a neutral position and 2.3% admitted to being insufficiently informed about the country.
“Denmark is perceived by Ukrainians as a sincere partner and reliable ally in the current circumstances. The high level of trust reflects both humanitarian aid and consistent political support for Ukraine from Copenhagen,” said Active Group CEO Oleksandr Pozniy.
Maksim Urakin, co-founder of Experts Club, analyzed trade and economic indicators:
“According to the results of January-August 2025, trade turnover between Ukraine and Denmark amounted to about $279 million. Exports of Ukrainian goods reached $109.3 million, while imports from Denmark exceeded $169.6 million. As a result, there was a negative balance of $60.3 million. This indicates that, despite very warm public sentiment, Ukraine should work to strengthen its exports to the Danish market,” the expert emphasized.
Thus, Denmark remains one of the most positively perceived countries among Ukrainians, but the economic component of relations requires more balanced development.
The full video can be viewed at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YgC9TPnMoMI&t
You can subscribe to the Experts Club YouTube channel here: https://www.youtube.com/@ExpertsClub
ACTIVE GROUP, DENMARK, EU, EXPERTS CLUB, Pozniy, SOCIOLOGY, TRADE, UKRAINE, УРАКИН

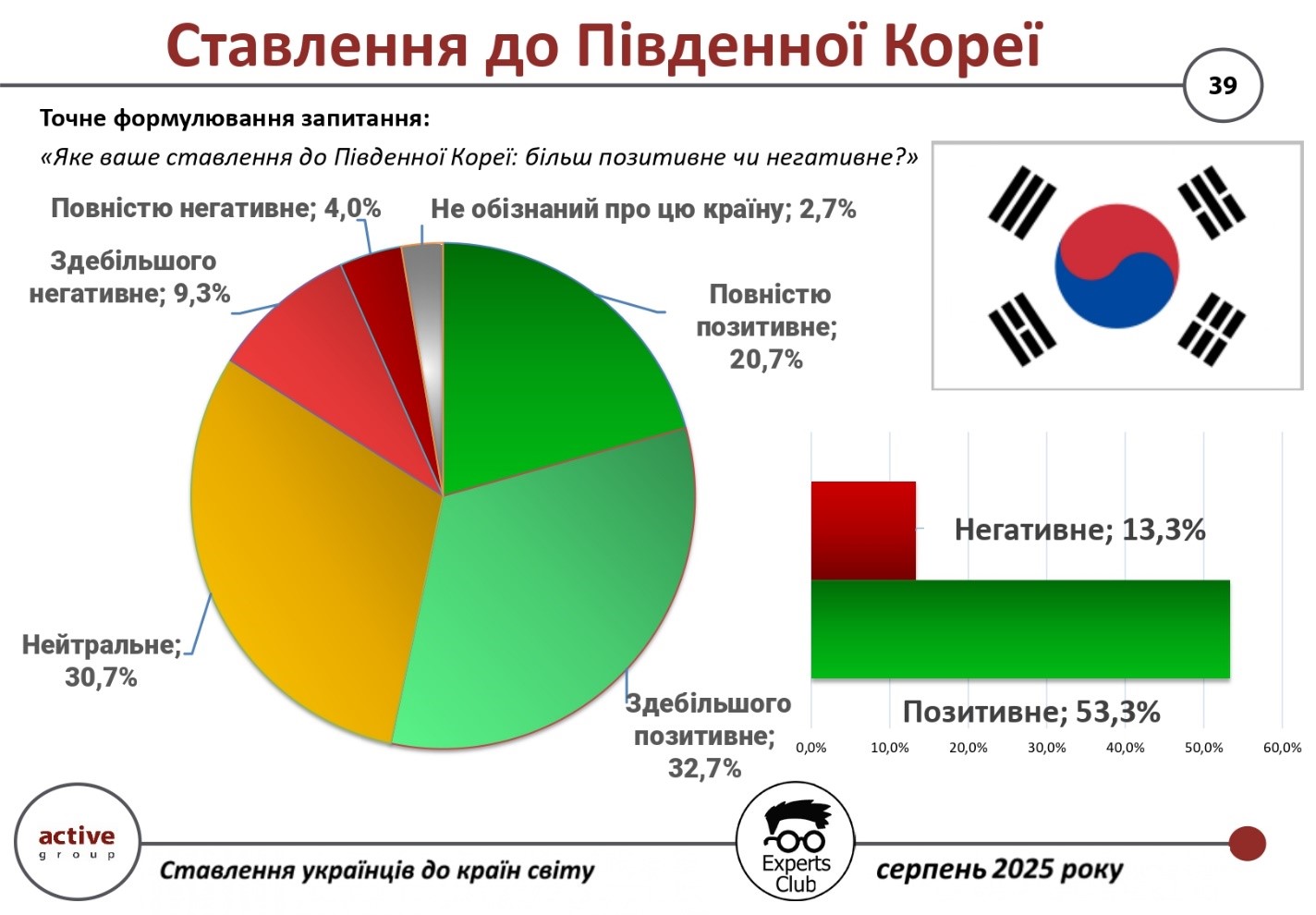
According to the results of a survey conducted by Active Group in collaboration with Experts Club in August 2025, more than half of Ukrainians have a positive opinion of South Korea.
In total, 53.3% of respondents expressed their favorability toward this country (32.7% — mostly positive, 20.7% — completely positive). A neutral attitude was recorded in 30.7% of respondents, while negative assessments accounted for 13.3%. Another 2.7% said they were not familiar enough with this country.
“South Korea is perceived by Ukrainians as a modern, high-tech country that is developing dynamically while preserving its cultural identity. Ukrainians see it as a potential partner, especially in the fields of technology, education, and innovation,” said Active Group CEO Oleksandr Pozniy.
At the same time, Maksim Urakin, co-founder of Experts Club, emphasized the economic dimension of bilateral relations:
“At the end of the first half of 2025, the total trade turnover between Ukraine and the Republic of Korea amounted to more than $518 million. Exports of Ukrainian goods amounted to only $96.9 million, while imports exceeded $421 million.
This resulted in a negative trade balance of $324 million. The situation demonstrates the need for more active promotion of Ukrainian goods on the Korean market, particularly in the agricultural and food sectors,” he stressed.
The study is part of the systematic monitoring of Ukraine’s international relations and public opinion regarding its partners in the world.
The full video can be viewed at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YgC9TPnMoMI&t
You can subscribe to the Experts Club YouTube channel here: https://www.youtube.com/@ExpertsClub
ACTIVE GROUP, EXPERTS CLUB, Pozniy, SOCIOLOGY, SOUTH KOREA, TRADE, UKRAINE, URAKIN

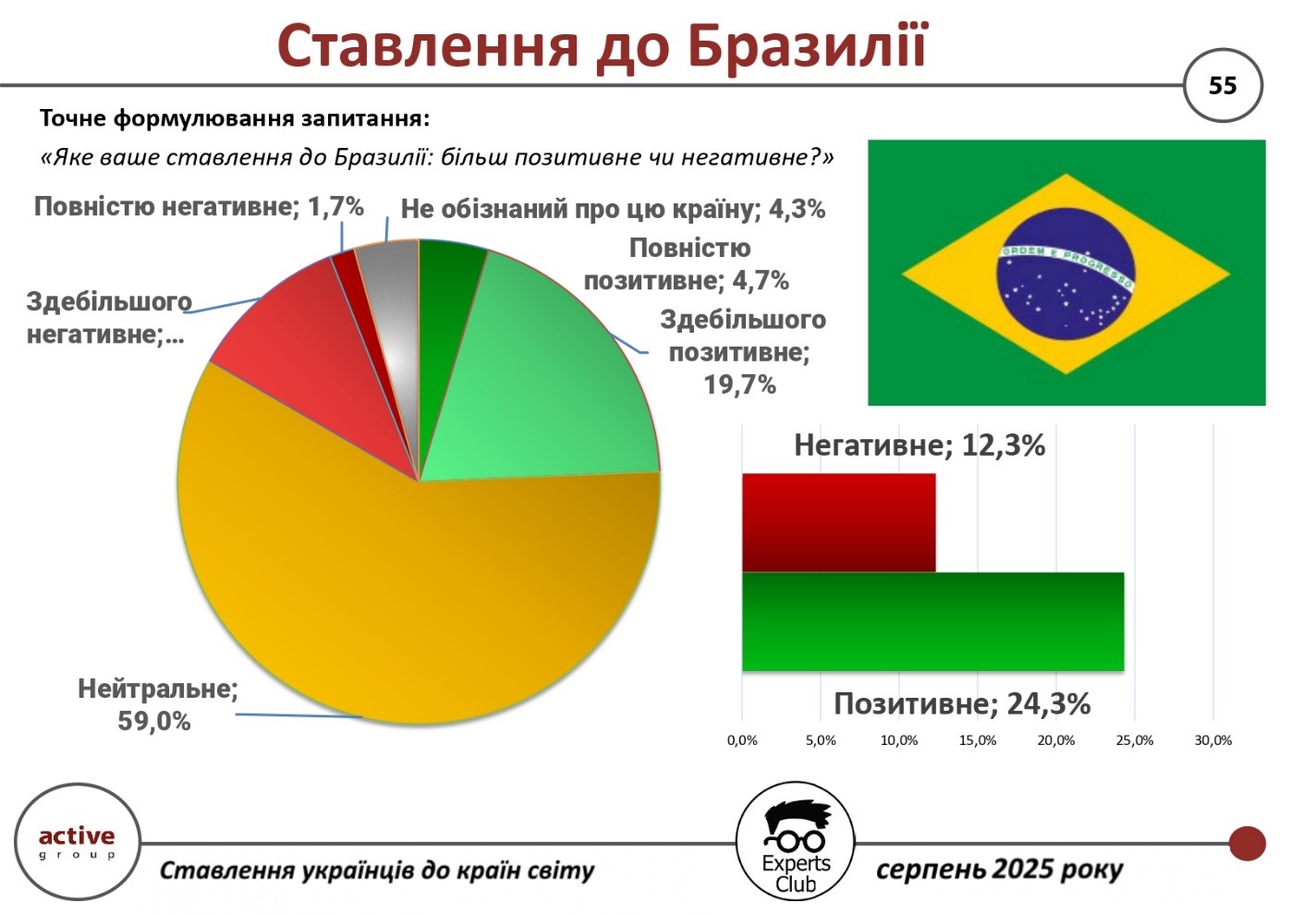
The majority of Ukrainians have a neutral attitude toward Brazil, according to a survey conducted by Active Group and the Experts Club.
According to the survey, 59.0% of respondents have a neutral position on the country. 24.3% of respondents have a positive attitude (in particular, 19.7% – “mostly positive” and 4.7% – “completely positive”). At the same time, 12.3% of Ukrainian citizens expressed a negative attitude toward Brazil, and another 4.3% said they were not familiar with the country.
Thus, the balance of positive and negative attitudes is +12 percentage points (24.3% vs. 12.3%).
According to the latest data, the volume of trade in goods between Ukraine and Brazil amounted to $180.3 million in 2024.
Ukrainian exports to Brazil amounted to $36.1 million,
– imports from Brazil amounted to $144.2 million,
– the negative balance was $108.1 million.
The total trade turnover reached $180.3 million, which indicates Ukraine’s significant dependence on Brazilian imports.
“Brazil remains an important trading partner for Ukraine in Latin America, but the structure of bilateral trade is currently asymmetrical. The significant deficit reflects the predominance of imports, in particular agricultural products and industrial goods,” said Maksym Urakin, economist and founder of Experts Club.
He emphasized that amid growing global competition, Ukraine should actively seek opportunities to increase exports to the Brazilian market: “This applies not only to agricultural products, but also to high-tech industries where Ukraine has competitive advantages.”
The full video can be viewed here:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YgC9TPnMoMI&t
You can subscribe to the Experts Club YouTube channel here:
https://www.youtube.com/@ExpertsClub
ACTIVE GROUP, BRAZIL, EXPERTS CLUB, Poznyi, SOCIOLOGY, TRADE, UKRAINE, URAKIN

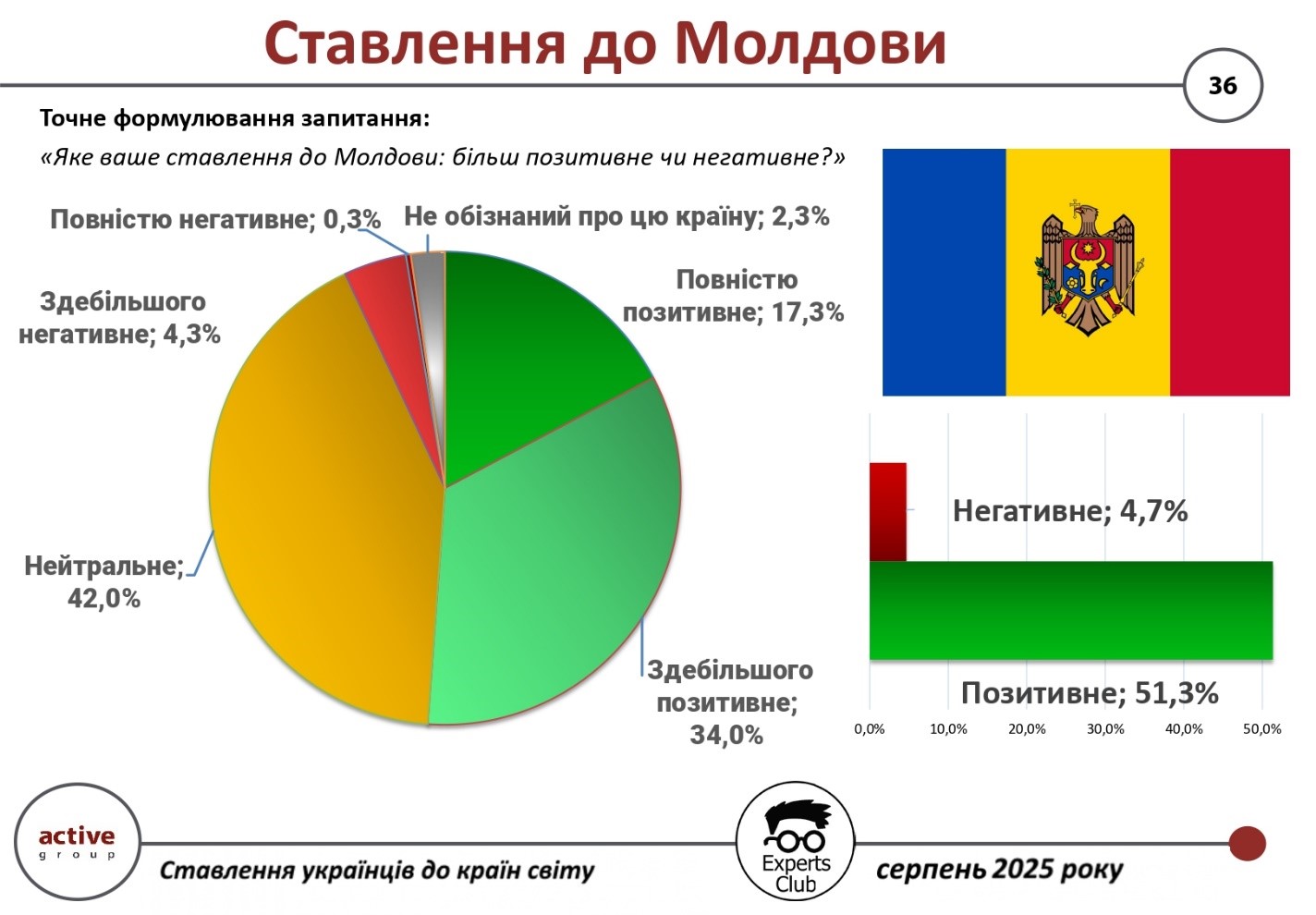
Most Ukrainians have a positive attitude toward Moldova, as evidenced by the results of a sociological study conducted by Active Group in collaboration with Experts Club in August 2025.
According to the data, 51.3% of respondents have a positive attitude towards the neighbouring country (34.0% — mostly positive, 17.3% — completely positive). Only 4.7% of respondents have a negative attitude (4.3% — mostly negative, 0.3% — completely negative). At the same time, 42.0% of citizens remain neutral, and another 2.3% said they did not have enough information about Moldova.
“Despite difficult historical relations and various political challenges, Ukrainians’ attitude towards Moldova is rather warm and friendly. This is explained by both geographical proximity and similar cultural traditions,” said Active Group CEO Oleksandr Pozniy.
In turn, co-founder of Experts Club Maksim Urakin emphasized the importance of economic cooperation between the two countries:
“In 2025, Ukraine maintains a significant positive trade balance with Moldova — over $448 million. Ukrainian exports amounted to about $519 million, while imports — only $70.9 million. The total volume of bilateral trade reached $590 million, and this dynamic indicates Moldova’s stable interest in Ukrainian goods,” he stressed.
The study is part of a large-scale project analyzing Ukraine’s international sympathies and economic relations.
The full video can be viewed at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YgC9TPnMoMI&t
You can subscribe to the Experts Club YouTube channel here: https://www.youtube.com/@ExpertsClub
ACTIVE GROUP, EXPERTS CLUB, MOLDOVA, Pozniy, RELATIONS, SOCIOLOGY, TRADE, UKRAINE, URAKIN

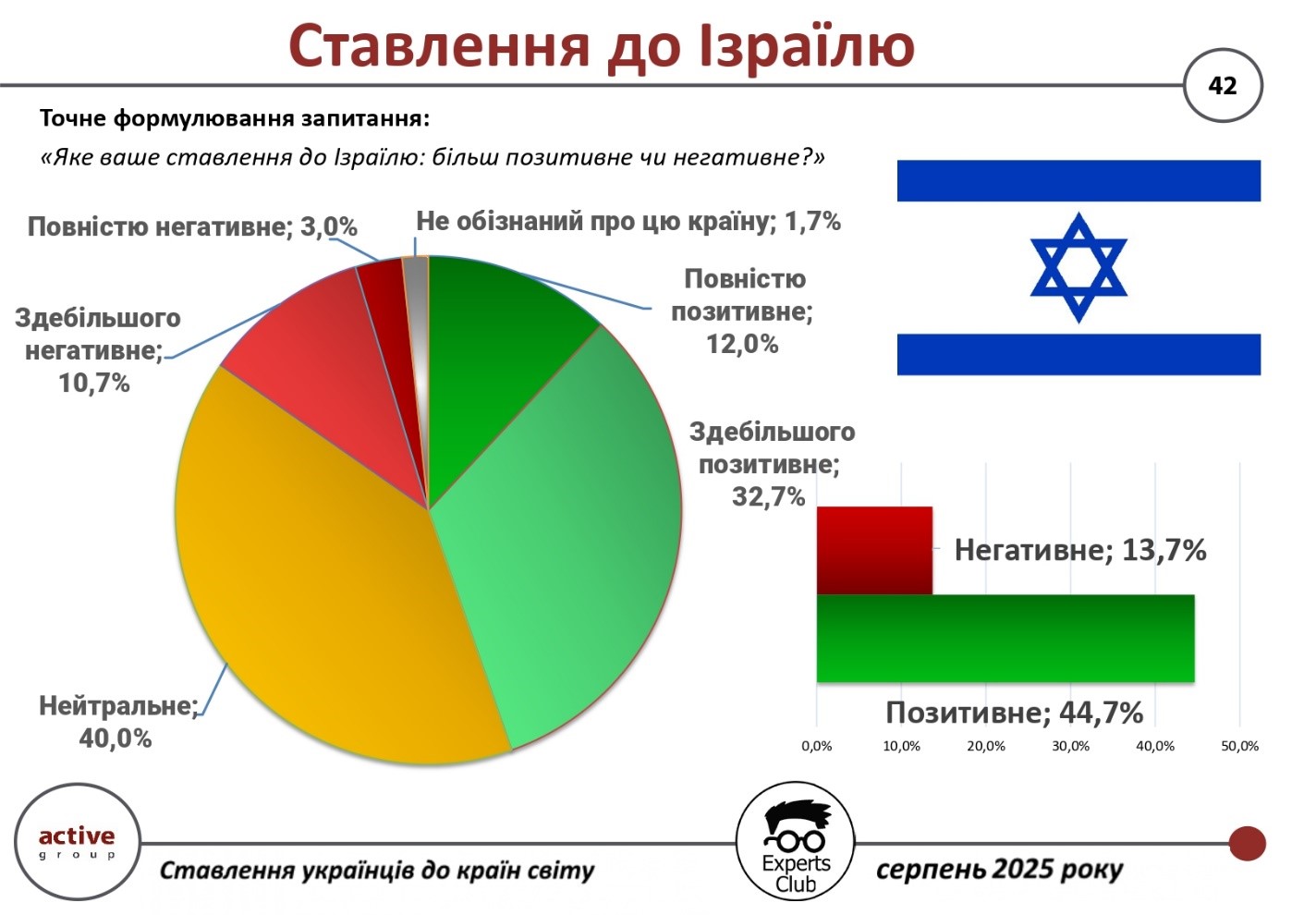
According to the results of a survey conducted by Active Group and Experts Club in August 2025, Ukrainians tend to have a positive attitude toward Israel.
Thus, 44.7% of respondents expressed sympathy for this country (32.7% — mostly positive, 12% — completely positive). Negative assessments accounted for 13.7%, another 40% remained neutral, and 1.7% admitted that they did not know enough about Israel.
“Despite a certain percentage of criticism, Ukrainians’ attitude toward Israel remains generally positive. This is explained by both historical ties and cooperation in the fields of medicine, science, and military technology,” commented Active Group CEO Oleksandr Pozniy.
In turn, Maksim Urakin, co-founder of Experts Club, drew attention to the trade and economic component:
“At the end of 2025, bilateral trade between Ukraine and Israel amounted to more than $353 million. Ukrainian exports amounted to $132.4 million, while imports of Israeli goods exceeded $221 million. This led to a negative balance of about $88.6 million. Such an imbalance indicates the need to expand Ukrainian exports and search for new niches in the Israeli market,” he stressed.
Thus, Ukrainians’ attitude toward Israel is moderately positive, but economic indicators show challenges that should be taken into account in bilateral relations.
The full video can be viewed at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YgC9TPnMoMI&t
You can subscribe to the Experts Club YouTube channel here: https://www.youtube.com/@ExpertsClub
ACTIVE GROUP, EXPERTS CLUB, ISRAEL, Pozniy, SOCIOLOGY, TRADE, UKRAINE, URAKIN